Cystitis: what causes it? Main reasons
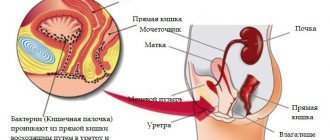
Patients with cystitis are almost always women. They are initially at risk due to the structural features of the body: the short and wide urethra, located near the vagina, opens wide opportunities for pathogenic microorganisms to enter the bladder. But this is only a probability, which is higher the more often a person encounters the following factors:
- Hypothermia. The habit of dressing inappropriately for the weather, swimming in low temperatures and sitting on cold surfaces almost always leads to cystitis. The blood vessels in the bladder narrow, which is beneficial for the development and further reproduction of bacteria in the tissues.
- Hormonal disbalance. We are talking about a sharp drop in estrogen in the body, which leads to problems with the genitourinary system. For this reason, cystitis often occurs in women during menopause.
- Disturbed blood flow in the pelvic organs. The majority of adults face this problem: sedentary work and minimal movement provoke an inflammatory process in the bladder.
- Stagnation of urine. Almost all people periodically have to endure, putting off going to the toilet “until better times”: a long queue, a long trip on a bus with no possibility of stopping, a closed bathroom on a train... But some unjustifiably risk their health, simply not wanting to get up from the computer to go to the toilet. This habit leads to the active development of infections in stagnant urine. As a result, not only cystitis is likely, but also bladder stones.
- Ignoring personal hygiene rules. Despite the availability of information, many women simply do not know how to care for their bodies. Necessary:
- wash yourself daily;
- change pads and tampons at least every two hours;
- after defecation, wipe from front to back (otherwise intestinal bacteria may enter the urethra and bladder);
- wash thoroughly before and after sexual intercourse;
- do not practice vaginal sex immediately after anal sex.
The above reasons do not necessarily provoke cystitis. If the body is strong enough, then it will be able to resist the disease and cope with it on its own, even without “notifying” the person. But a slight decrease in immunity (for example, during a cold or during pregnancy) can become the trigger that activates all the symptoms of cystitis.
Routes of infection
If a patient experiences cystitis after sex, this indicates sexual transmission of infection, in particular bacteria. There are other ways of infection:
- ascending. Bacteria enter the bladder through the urethra. This route of transmission is the most common;
- descending. The infection descends into the bladder from the kidneys, for example, with pyelonephritis;
- lymphogenous. Transmission of infection occurs through lymph. In women, this usually occurs with inflammation of the appendages;
- straight. The infection enters the bladder during surgery, installation of a catheter, or when ulcers break through in the tissues surrounding the organ.
Depending on the cause and route of infection, the doctor will choose a specific remedy for cystitis.
What causes cystitis? Nutrition issues
The body reacts very sensitively to what it is fed. And the body does not like the following foods too much:
- alcohol;
- hot spices;
- citrus fruits and juices from them;
- carbonated drinks;
- onion;
- some fruits and berries (for example, grapes, melons, peaches, apples, plums);
- cheese products;
- mayonnaise, soy sauce, vinegar;
- chocolate;
- nuts.
These foods irritate the bladder, increasing the risk of bladder inflammation. This also includes medications and vitamins that contain saccharin.
Some people can tolerate “dangerous” foods just fine, but it is best to limit the amount of them in your diet to minimize the likelihood of developing cystitis.
Treatment of cystitis with folk remedies
Read also Diabetes mellitus. Symptoms, causes and treatment of diabetes
Many, many people have been helped by folk remedies in the treatment of cystitis. Let's look at some of them.
Warming up
Before warming up, it will be good if you steam your legs, and then, after wrapping yourself up, apply a heating pad to the bladder area.
Salt. Heat table salt in a frying pan and pour into a sock. Apply it like a heating pad to your lower abdomen and crawl under the blanket.
Buckwheat, millet, rice. Do the same as with salt.
Water bottle. Fill a plastic bottle with hot water, apply it to your lower abdomen and wrap yourself up.
The warming process should be pleasant, so if the heating pad is very hot, place a cloth under it.
Baths
With sea salt. Fill the bath with water and add sea salt.
With essential oils. Add 2 drops each of eucalyptus, sandalwood and juniper oils to the bath water and sit for 10 minutes.
Juniper essential oil is contraindicated during pregnancy.
With chamomile. Brew 3-4 tbsp in boiling water. spoons of chamomile and pour into a bowl, stirring with warm water. Sit in this bath until it cools down, but remember that the water should not be too hot. You can make the same bath with calendula or add calendula to chamomile.
With iodine. Fill a bowl of hot water and pour in some iodine. Sit over the bath for 10-15 minutes.
With milk. Heat the milk to such a state that you can sit in it, take it until it cools down.
Decoctions
Chamomile. Pour 1 tbsp. spoon of chamomile 1 glass of boiling water. Take 20 ml 3 times a day.
Read also Encephalitis - symptoms, causes, treatment and prevention of encephalitis
St. John's wort. 1 tbsp. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over a spoonful of St. John's wort. Boil for 10-15 minutes and strain. Take 50 ml 3 times a day.
Sage. 1 tbsp. Pour a spoonful of medicinal sage into 1 cup of boiling water and boil for 30 minutes in a water bath. Cool and add hot water if necessary until you get 1 cup of liquid. Take 50 ml 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Lingonberry leaves. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over 2 teaspoons of lingonberry leaves and boil for 10-15 minutes. Let the broth steep for at least 2 hours. Strain and take 100 ml 4 times a day before meals.
Yarrow. Brew 2 teaspoons of yarrow with 1 cup of boiling water. Let stand for 1 hour and strain. Take a quarter glass 4 times a day.
Psychological causes of cystitis
All sober-minded people sooner or later understand that the psychological state directly affects physical well-being. The main “reasons” for cystitis from this point of view include:
- Anger. It is believed that the body is trying with all its might to remove negative emotions from itself. And urine “contaminated” with anger becomes a favorable springboard for the development of infection.
- Fear of life and free will. Many suffer from the fear of quitting their job, moving away from their parents, leaving a boring partner... As a result, a person shrinks internally, which negatively affects the general condition of the body.
- Nervousness, constant feeling of anxiety. Frequent stress has long been considered one of the factors provoking illness. Strong experiences weaken the immune system: the slightest “hint” is enough – and cystitis will begin to actively develop.
Of course, it is hardly possible to completely get rid of negativity in the modern world. But when your own health is at stake, it doesn’t hurt to at least try.
Causes of cystitis in women: why and what causes cystitis, symptoms, treatment
The causes of cystitis in women, as well as in men, have been studied in detail. It is detected early and treated successfully. By understanding what and why cystitis occurs, you can prevent its occurrence.
Causes of cystitis in women
Before we move on to identifying the cause of cystitis, let’s understand how it manifests itself.
Symptoms of cystitis in women:
- painful urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- a feeling that the bladder is still full after urinating;
- urinary incontinence;
- change in urine color to a cloudy, reddish hue.
Causes of cystitis in women:
- Hypothermia of the pelvic area.
- Injury to the mucous membranes of the bladder.
- Sedentary, especially sedentary lifestyle.
- Poor diet, rich in fatty and spicy foods.
- Gynecological and venereal diseases.
- Unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Poor hygiene.
The symptoms of cystitis in men are the same, the only difference is an increased burning sensation when urinating, as well as the presence of mucus in the urine. The causes of cystitis in men have a number of differences from women:
- It often develops against the background of concomitant diseases (prostatitis, epididymitis).
- Complications of diseases such as purpura, schistosomiasis.
- Most often caused by chlamydia, trichomonas and gonococcus.
The causes of acute cystitis in women are mainly opportunistic flora penetrating from the vagina or intestines. These are Escherichia coli, Proteus, and Candida fungi. But sometimes cystitis occurs due to pathogens: gonococcus, herpes, trichomonas, and chlamydia.
Manifestations of acute cystitis may disappear on their own within three days. This is due to the fact that the body’s protective functions come into play, and the general condition remains satisfactory, there is no increase in temperature or weakness. But at the same time there is:
- urinating too frequently;
- sharp pain in the perineum;
- the presence of blood in the urine or a change in its color;
- nausea.
Sometimes a violation of the integrity of blood vessels can explain the causes of cystitis with blood, which is frightening and causes a lot of inconvenience. As you can see, the causes of cystitis in women can be prevented by following simple rules.
What causes cystitis in women and girls
Cystitis can occur even with proper hygiene and compliance with all rules. Cystitis occurs in women due to the following three pathogens: bacteria, fungi, viruses.
In addition to all this, there are a number of factors that can aggravate cystitis or trigger the process of pathogen reproduction:
- kidney diseases;
- addiction to spicy foods;
- presence of stones in the bladder;
- frequent constipation;
- colds or any infectious diseases;
- sexual life (if basic hygiene rules are not observed, indiscriminate changes of partners).
Cystitis is relatively easy to treat; treatment of cystitis in women involves:
- Drink plenty of warm drinks.
- Proper nutrition, excluding large amounts of salt and spicy foods.
- Quitting alcohol.
- Taking antibiotics and medications prescribed by a doctor that will help eliminate the cause of cystitis, as well as the symptoms of the disease.
Chronic cystitis: causes
In about a third of cases, acute cystitis passes into the chronic phase. This means deeper damage to the bladder, as well as the likelihood of irreversible changes in the muscle layer and shrinkage of the organ.
The causes of chronic cystitis are traditionally called:
- Complication from another disease. Infection from the affected organ spreads throughout the body, reaching the bladder. Most often, this route passes through the kidneys. Without eliminating the initial source of inflammation, it is impossible to cure chronic cystitis.
- Factors provoking acute cystitis. This includes poor hygiene, weak immunity, hormonal changes, and hypothermia. But impaired bladder emptying is especially critical.
- Advanced or untreated acute cystitis. If the patient has undergone incomplete or poor-quality treatment, then the likelihood of the disease degenerating into a chronic form is almost guaranteed.
In fact, in the international classification the concept of “Chronic cystitis” as such is absent, but there is “Other chronic cystitis”. This means that the doctor must definitely detail the diagnosis, finding the original cause of the inflammation and taking care of bringing the problem organ back to normal. Only against the background of such therapy is it possible to successfully treat the bladder.
The causes of cystitis are mainly related to poor lifestyle. It is enough to eat a balanced diet, move more and promptly “respond” to the urge to urinate to significantly reduce the likelihood of cystitis. Following these simple recommendations will not cause any discomfort, but will improve your well-being and improve your overall quality of life.
What causes cystitis in women? Causes, methods of treatment
Cystitis is a fairly common disease that doctors often deal with. By the way, according to statistical studies, representatives of the fair sex are more susceptible to this disease.
It is quite natural to ask what causes cystitis in women and what factors can trigger the disease.
Patients are also interested in diagnostic and treatment methods offered by modern medicine.
What is "cystitis"?
Before considering the question of why cystitis often occurs in women, it is worth understanding what this disease is. Cystitis is a disease that is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the walls of the bladder.
It is believed that this is a kind of “women's disease”. Naturally, men are also susceptible to this kind of disease, but 80% of patients with this diagnosis are representatives of the fair sex between the ages of 20 and 40.
What causes cystitis in women and why are they so susceptible to the disease? The features of female anatomy are important here, because the anus and vagina are located very close to the urethra, and the canal itself is wider and not as long as in men, which is why infection from the outside penetrates into the genitourinary organs much more often.
Many patients face a similar diagnosis. But before considering treatment methods, it is worth finding out what causes cystitis in women. In most cases, inflammation develops against the background of active bacterial infection. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the tissues of the reproductive system from the external environment, and can spread from other foci of inflammation.
In fact, there are a huge number of factors that can provoke an inflammatory process in the bladder:
- Previously suffered infectious diseases with a chronic or acute course. This could be salpingitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, adnexitis, sexually transmitted diseases.
- Anatomical features of the female genitourinary system, for example, strictures.
- Oncological diseases can also interfere with the normal excretion of urine, causing stagnation, which, accordingly, creates ideal conditions for the proliferation of bacteria.
- Severe hypothermia of the body.
- Decreased immune activity, including during pregnancy.
- “Sedentary” work, since in this position there is often stagnation of urine and other fluids in the pelvis.
- The presence of chronic foci of infection, including, for example, caries, chronic tonsillitis and rhinitis.
- Diabetes mellitus, which affects the functioning of the immune system.
- Constant stress and nervous strain (affect the immune system).
- Taking medications that suppress the activity of the immune system.
- Failure to comply with intimate hygiene standards.
- Chronic lack of sleep, poor diet.
- Elderly age.
- Early onset of sexual activity, frequent change of partners.
- Injuries to the genital organs and damage to the lower back.
It is very important to know what causes cystitis in women. Treatment in most cases depends on the root cause. This is why a thorough diagnosis is so important.
In modern medicine, there are several classification schemes for this disease. So what kind of cystitis occurs in women? Depending on the cause, there are:
- Infectious cystitis caused by the activity of pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses.
- Non-infectious inflammation can be triggered by an allergic reaction, taking medications or toxins entering the body, or undergoing radiation therapy.
Depending on the type of infection, cystitis is divided into:
- Specific, which is caused by the penetration of pathogens of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and ureaplasmosis into the body.
- Nonspecific cystitis is caused by activation of conditionally pathogenic microflora of a woman’s body, for example, E. coli, staphylococci, streptococci.
Depending on the course, acute and chronic forms of the disease are distinguished. Cystitis can be primary or secondary (occurs as a complication of another disease).
Modern diagnostic methods
If you have symptoms, you should definitely consult a specialist. To begin with, the doctor collects an anamnesis. Patients are advised to undergo a gynecological examination, as well as consultation with a therapist and urologist.
Diagnostics includes several laboratory tests, in particular, a vaginal smear to determine microflora.
You also need to donate blood and urine samples - this way you can detect the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
Bacteriological culture is required to isolate the pathogen and check its sensitivity to antibacterial agents. Next, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is performed. Sometimes doctors additionally prescribe cystoscopy (which makes it possible to evaluate the condition of the bladder from the inside) and urography.
How is cystitis treated? Drug therapy
During the diagnostic process, it is very important to determine what causes cystitis in women. Treatment directly depends on the cause of the development of the inflammatory process and the general condition of the patient’s body.
Therapy in this case must be comprehensive. If cystitis is caused by the activity of bacterial microorganisms (which occurs in 80% of cases), then the patient is prescribed antibacterial agents. Preference today is given to fosfomycin and nitrofurans, since they accumulate well in the urine and act on the most common pathogens of cystitis.
For bacterial cystitis, it is advisable to carry out a course of therapy with antimicrobial drugs that are well excreted in the urine and act on E. coli, the most common causative agent of cystitis.
When treating cystitis, especially recurrent cystitis, a single use of an antibiotic is not enough, since pathogenic microorganisms quickly develop resistance. For example, E. coli has become resistant to many types of antibiotics.
As a result, the dosage of antibiotics has to be constantly increased.
The drug Macmiror belongs to the category of antimicrobial agents with antibacterial, antifungal and antiprotozoal effects, and due to the properties of its molecule, microbes have practically no resistance to it.
In case of recurrent cystitis, examination by a gynecologist is also recommended and, if vaginitis or bacterial vaginosis is detected, Macmiror Complex vaginal capsules can be applied topically along with an antimicrobial drug orally. This increases the effectiveness and speed of healing. And the fact that untreated gynecological infections can influence the frequency of cystitis relapses is a proven fact in medicine.
The treatment regimen must include uroseptic drugs, in particular Furagin and Canephron. For cystitis, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often used, for example, Ibuprofen, Ibufen, Nurofen, Paracetamol.
Sometimes, to alleviate the patient’s condition, “No-spa” is used, which relieves spasm of smooth muscles.
Since antibiotics negatively affect beneficial microflora, probiotics are used to protect them, in particular Bifiform, Linex, Acipol.
Other types of treatment and useful tips
In some cases, along with conservative therapy, women are also recommended thermal procedures. It is recommended to avoid salty and spicy foods, spices, chocolate and coffee during treatment. It's also important to drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
Physiotherapy is usually used in the treatment of chronic forms of cystitis. And in such cases, mud applications, UHF procedures, electrophoresis with the use of drugs, iontophoresis (antiseptics and nitrofurans are used) are effective.
Possible complications of the disease
Now you know what causes cystitis in women (with blood). Treatment in most cases goes smoothly. Complications develop if therapy was carried out incorrectly or was completely absent.
The infection can spread to other tissues, in particular to the muscle layer of the bladder - this form of cystitis is much more difficult to treat.
The inflammatory process often spreads to other organs of the genitourinary system, provoking the development of nephritis and other diseases.
The most dangerous complications include bladder rupture followed by peritonitis - fortunately, this is extremely rarely recorded in modern medicine.
Why does cystitis occur in women after sex?
Quite often, inflammation of the bladder develops in the fair sex after sexual intercourse. Popularly, this phenomenon even has its own name - “honeymoon syndrome.” Often, cystitis develops immediately after the first sexual experience, as the usual vaginal microflora changes.
Why do women often experience cystitis after sex? In fact, there can be many reasons. For example, not all partners adhere to the rules of hygiene before and after intercourse (this applies not only to women, but also to men). Tissue infection can occur due to failure to use condoms.
Prolonged sexual intercourse, especially in the absence of a sufficient amount of lubrication, injures the vaginal mucosa, which creates excellent conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and their migration through the genitourinary system.
Risk factors also include the use of contraceptives that change the normal composition of vaginal discharge.
Is treatment at home advisable?
Today, many patients are interested in the question of what causes cystitis in women and how to treat it at home. Today, a huge number of folk recipes are known, but it is worth understanding that you can use any means only after consulting a doctor. Inept use of home recipes can lead to a lot of unpleasant and dangerous consequences.
Quite often, thermal procedures are recommended to help relieve pain. For example, you can put a heating pad on your lower abdomen or prepare a sitz bath from a decoction of medicinal plants (sage, chamomile flowers, and string herb are suitable). Tea made from red rowan bark is considered beneficial (boil 100 g of bark in a liter of water).
Taking echinacea may be helpful. By itself, this remedy cannot cure cystitis, but the tincture of this plant stimulates the activity of the immune system, which speeds up the healing process.
Prevention of cystitis: useful recommendations for women
Now you know what causes cystitis in women and how to treat it. But, you must admit that it is much easier to prevent the development of the disease than to then undergo therapy and cope with the consequences. There is no specific preventative measure, but women are advised to follow some rules.
As you know, quite often the cause of inflammation is infection, which is why patients are advised to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene and refuse to wear panties - thongs or any underwear that is too tight. It is very important to use condoms during sexual intercourse. You should avoid hypothermia and dress appropriately for the weather. Women are also advised to maintain good hygiene and undergo routine medical examinations.
There are contraindications. It is necessary to read the instructions for use.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/288616/ot-chego-byivaet-tsistit-u-jenschin-prichinyi-sposobyi-lecheniya