- February 17, 2019
- Climax
- Vladislav Bulkin
Some women really look forward to the onset of menopause after 60 years, since at this time many gynecological problems are minimized, significantly reducing the activity of their manifestations. The situation is completely different with an ovarian cyst, which forms in a woman after reaching 60 years of age. Undoubtedly, this new growth should cause concern. Read more about why an ovarian cyst is dangerous after 60 years, the treatment of which is mainly surgical.
Where does the cyst come from?
Due to certain disorders in the body of a woman of retirement age, the follicle may not rupture, without releasing the egg, forming a follicular-type cyst. This is a neoplasm with thin walls that has liquid contents. The causes of ovarian cysts after 60 years, the treatment of which is difficult, are very diverse.
Follicular cysts reach an average size of about 6 cm or even more. They have a single-chamber structure, but sometimes several cysts can form simultaneously in the ovary. This creates a multi-chamber structure. Functional cysts usually occur in menstruating women and go away on their own.
Types of cysts
Not all cysts can be called true. True cysts increase not as a result of the division of cells that form the wall, which is noted with the development of tumors of other types, but due to excessive stretching of their walls.
Therefore, an ovarian cyst is a neoplasm of the corpus luteum. This is a paraovarian or follicular cyst, and without proper treatment it can become malignant. Dermoid and mucinous cysts are a relatively harmless tumor that occurs in the ovaries at retirement age. An endometrioid type cyst in certain cases can cause the development of ovarian endometriosis.
So, the following types of cysts that occur in women over 60 years old are distinguished:
- A follicular cyst usually goes away without much treatment after a few menstrual cycles.
- Mucinous can reach truly enormous sizes (about 8 kg). It consists of mucous-type secretions.
- A dermoid cyst fills with skin, hair, and even bones.
- Endometriotic - in this case, monthly menstrual tissue, which is located in the uterus, passes into the ovary, as a result of which the cyst begins to fill with brown, old blood.
- Polycystic - there is an accumulation of follicular cysts, and most often this type occurs in patients with polycystic syndrome. But even completely healthy women approaching retirement age can suffer from polycystic disease.
- The development of paraovarian and other types of cysts is possible.
Causes of the disease
Typically, ovarian cysts develop in women of childbearing age, as this is due to the characteristics of their hormonal levels. Initially, they talk about formations of a functional type, usually disappearing after several menstrual cycles. But the appearance of cysts is not affected in any way by cyclic changes. At the age of over 60 years, cystic neoplasms can cause a lot of problems for women.
Many women are surprised that the cyst arose precisely at retirement age. But, undoubtedly, this phenomenon is justified in some way. During menopause, the body may experience a decrease in the production of certain female hormones. Because of this, a woman’s reproductive organs gradually lose their normal functions.
It is known that the ovaries do not function fully, this can cause the appearance of quite dangerous foreign inclusions. After 60 years, a woman cannot develop functional formations, since ovulation does not occur. An ovarian cyst can appear for a variety of reasons, but it is quite difficult to determine its exact cause.
The following factors are known that can increase the likelihood of cysts appearing in the ovaries:
- improper functioning of the ovaries;
- age over 50 years;
- early menopause;
- no pregnancy;
- frequent inflammations in the genital area;
- bloody issues.
Lazy ovaries
Ovarian hypofunction is a group of pathological conditions that are manifested by weakened functionality of these organs. You need to understand that hypofunction is not a clinical diagnosis, but the result of the progression of various pathologies both in the ovaries and in the organs that control their function.
Functions
The ovaries are paired female sex glands and perform the following functions:
- Generative. It consists of ensuring the maturation of female germ cells, that is, maintaining the ability to conceive.
- Vegetative. It consists in the formation of the female phenotype, that is, in ensuring the correct development of secondary characteristics of the female sex.
- Hormonal. It consists of the cyclic production of progesterone and estrogen under the control of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
In the body of a healthy woman of reproductive age, an egg matures monthly. During this process, the egg is located in the follicle.
The maturing follicle has a stimulating effect on estrogen production.
The complete development of the egg in the first phase of the cycle is ensured by FSH - follicle-stimulating hormone, which is produced in the pituitary gland.
During the ovulatory period, a mature egg is released from the follicle, and the corpus luteum is formed in its place.
From this moment, within two weeks, it produces progesterone, which is necessary for the correct course of pregnancy if conception occurs. If fertilization of the egg does not occur, then the destruction of the corpus luteum occurs.
In the next cycle it is formed again. The second half of the cycle is under the control of LH - luteinizing hormone.
Simultaneously with the cyclic processes in the ovaries, the endometrium grows in the uterus in the first phase of the cycle, and is rejected in the second. With hormonal imbalances, pathological changes also affect the endometrium. Therefore, for any symptoms of dysfunction in the reproductive system, its health is assessed comprehensively.
The nature of the menstrual cycle is a criterion for assessing the correct functioning of the ovaries. The presence of ovulation and a two-phase cycle indicate the proper functioning of these organs.
Causes
Hypofunctionality of the ovaries can accompany many diseases of the reproductive system, associated both with changes in the tissue of these organs itself, and with disorders in the central part of the endocrine system. Hypofunction can be primary or secondary.
Primary hypofunction is associated with disturbances in the processes of intrauterine development of the female body. Congenital underdevelopment of the ovaries may be a consequence of the mother's history of measles or rubella. It is also possible due to hormonal imbalance in the mother’s body, due to hereditary diseases in the expectant mother and due to psycho-emotional disorders she has suffered.
Secondary hypofunction can be triggered by factors listed below:
- A sharp decrease in body weight as a result of the progression of somatic pathologies or due to anorexia nervosa.
- Poor nutrition, which does not contain enough vitamins and fats.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the ovaries (oophoritis, adnexitis).
- Pathologies of the pituitary gland and/or hypothalamus, provoked by traumatic brain injury, psycho-emotional disorders, and cancer of the brain.
- Diseases of the endocrine system affecting the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
- Oncopathologies and polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Ovarian wasting syndrome.
- Uncontrolled long-term use of oral contraceptives.
Thus, ovarian hypofunction is a polyetiological condition, therefore, when it is identified, a comprehensive diagnosis is required to determine the exact cause and the appropriate method of correction.
Symptoms
Clinically, hypofunction is manifested by a disrupted menstrual cycle, reverse development of secondary sex characteristics, as well as infertility. In the case of primary hypofunction, the organs of the reproductive system remain underdeveloped. It is worth noting that the decrease in ovarian function during menopause is physiological.
The basis of the pathogenesis of hypofunction is hypoestrogenism - reduced production of estrogen. The clinical consequences of this condition are presented in the table.
The nature of clinical symptoms depends on the degree of hypofunction:
- Easy. The size of the uterus is normal or slightly reduced, the endometrium is formed correctly, but is not developed enough. Satisfactory development of secondary sexual characteristics. Irregular (less often than acceptable) and scanty menstrual bleeding, in some cases - amenorrhea.
- Average. Amenorrhea, underdevelopment of the external genitalia and mammary glands. The size of the ovaries and uterus is significantly smaller than the age norm.
- Heavy. It is quite rare. It is characterized by underdevelopment of the genital organs, the absence of secondary characteristics of sex, and primary amenorrhea.
Hypofunctional states that developed after the normal course of puberty are characterized by mild clinical symptoms. Hypofunction in this case manifests itself as cycle disorders: menstrual bleeding becomes short and scanty, and the interval between them gradually increases.
Without therapeutic correction, atrophic changes in the endometrium, amenorrhea, a decrease in the size of the ovaries and uterus develop, and psychoemotional disorders are also observed.
Diagnostics
Examination of a patient with manifestations of ovarian hypofunction should include:
- examination (assessment of physique, determination of the development of the genital organs and secondary sexual characteristics and the compliance of these parameters with age standards);
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- laboratory studies of hormonal status.
Some additional diagnostic procedures may also be required depending on the characteristics of the clinical case. Only after identifying the provoking pathology and the degree of its severity can the doctor prescribe a course of therapeutic correction.
Treatment
What to do if the ovaries do not work? The answer to this question can be given by a specialist after a complete examination of the patient. Timely identified secondary hypofunction responds well to treatment, but with the primary nature of this condition, a full restoration of the functional state of the ovaries is unlikely.
Therapy of hypofunctional conditions is a complex, lengthy and multi-stage process. The first stage is to stimulate puberty in the case of pre-pubertal ovarian hypofunction. It involves the administration of estrogens in a cyclical manner to ensure that developmental processes are similar to natural ones.
At the same time, attention is paid to eliminating negative factors: infectious pathologies, stress, somatic diseases and others. The duration of the first stage is determined by the doctor.
If, in response to these measures, the uterus increases in size and signs of normal ovarian activity are recorded, then the second stage of therapy is carried out. It is needed in order to form cyclic changes in the ovaries.
The patient is prescribed hormonal medications according to the phases of the cycle. With their help, the menstrual cycle is reliably simulated so that the “lazy” ovaries begin to work.
Progesterone-containing drugs are added to estrogen-containing drugs.
The effectiveness of treatment must be monitored using ultrasound and laboratory diagnostic methods. The criterion that the treatment is effective is the identification of follicles at the stage of maturation and the recording of cyclic changes in the endometrium.
The goal of the third stage is to achieve an ovulatory two-phase cycle. The success of therapeutic measures depends on the severity of hypofunction. The fourth stage consists of rehabilitation measures and prevention of relapses of the hypofunctional state. It involves regular visits to the doctor and monitoring of the hormonal function of the ovaries.
Source: https://dou99.ru/yaichniki/lenivye-yaichniki
Cyst symptoms
During menopause, a cyst affecting the ovaries may usually have no special symptoms, it is small in size, and causes minimal discomfort. Most often, this neoplasm can be detected by ultrasound or palpation. A gradual increase in the diameter of an ovarian cyst in women, the symptoms (treatment for which the doctor will prescribe) are as follows:
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen, aggravated by active movement and sexual intercourse;
- the desire to empty the intestines when the cyst is compressed;
- the occurrence of hemorrhoids;
- varicose veins due to compression of the vessels of a cystic neoplasm;
- feeling of heaviness and distension in the abdomen.
Sometimes a cyst-like formation can rupture or twist, and this is a dangerous condition for a woman’s health and even her life. In this case, the pain syndrome intensifies, the body temperature rises, and vomiting may even begin. An excessively enlarging cyst contributes to an increase in the volume of the abdomen and its protrusion. In particularly difficult cases, a woman over 60 years of age develops ascites.
If the cyst appears as a result of hormonal problems, the patient may experience the appearance of quite profuse bloody vaginal discharge, which, however, resembles menstruation, but is characterized by a lack of regularity.
Ovaries do not work: symptoms, causes, treatment
If the functioning of the reproductive organs is disrupted, then a woman cannot conceive and bear a child. To normalize reproductive function, you need to undergo treatment and find out the true reason why the ovaries do not work.
How does the malfunction of the appendages manifest itself?
Lazy ovaries cause a lot of problems. Patients suffering from infertility often have hormonal imbalances, which cause cycle disruptions.
Signs of normal functioning of the reproductive system:
- duration of menstruation from 4 to 10 days,
- interval between cycles 21-35 days,
- total blood loss during one menstruation is no more than 150 ml.
Ovarian dysfunction is often caused by hormonal problems and is manifested by a lack of ovulation and, as a consequence, infertility. A woman experiences irregular periods and bleeding between cycles. Menstrual flow is scanty.
Reasons why ovarian function is disrupted in women
Improper functioning of the appendages is noted as a result of:
- hormonal abnormalities, including PCOS,
- inflammatory processes,
- the presence of cystic formations, polyps, endometriosis,
- the use of certain medications,
- underweight
- diabetes, obesity (diseases provoke hormonal imbalance, which is reflected in the functioning of the ovaries),
- negative factors: changes in climatic zones, exposure to radiation, etc.,
- miscarriage or abortion,
- improper insertion of the intrauterine device.
Symptoms that the ovaries are not working well
The main cause of dysfunction of paired organs is a disruption in the production of sex hormones, provoked by deviations in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system. In this case, anovulation and luteal phase deficiency are observed, caused by excessive amounts of estrogen and progesterone deficiency.
Signs that the ovaries are not working include:
- irregular, scanty or heavy menstruation,
- bleeding between cycles
- miscarriage,
- infertility,
- dull and cramping pain in the lower abdomen, lower back (before menstruation, during it and during ovulation),
- pronounced PMS, accompanied by emotional problems,
- the interval between menstruation is less than 21 or more than 35 days, blood loss per cycle is more than 150 ml, bleeding lasting from 7 days,
- amenorrhea.
Diagnosis of pathology
To identify a malfunction of the ovaries, you need to contact a gynecologist. If he suspects hormonal causes of deviations, he will definitely refer you to a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
Diagnostic measures include:
- examination on a gynecological chair,
- anamnesis collection,
- exclusion of chronic reproductive diseases,
- Ultrasound of the pelvic region, thyroid and adrenal glands,
- examination of a vaginal smear for microflora,
- test for sexually transmitted diseases,
- determination of the concentration of sex hormones,
- radiography of the skull, CT and MRI of the brain,
- EEG to detect abnormalities
- hysteroscopy with cervical biopsy,
- curettage of the canal and cavity of the reproductive organ for histological examination of endometrial tissue.
Treatment of lazy ovaries
If there is no menstruation, then a detailed diagnosis is carried out, after which treatment is carried out. Therapy should be aimed at eliminating the root cause of deviations and combating concomitant diseases (diabetes mellitus, cystic formations, tumors, etc.). Additionally, vitamin and mineral complexes, massage, and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
If a woman suffers from obesity, then she is recommended to follow a diet and change her usual lifestyle. If you are underweight, measures are taken to normalize your weight. This allows you to restore ovulation and normal characteristics of the menstrual cycle. Then, when dysfunction of the appendages is caused by hormonal imbalance, a more serious approach is required.
So, with PCOS, if the patient does not plan a pregnancy, oral contraceptives are prescribed to even out the menstrual cycle and eliminate the symptoms of hormonal imbalance. For amenorrhea, the use of Duphaston is recommended. After a course of the drug, withdrawal bleeding begins, which is regarded as another period.
If PCOS is accompanied by an increase in blood sugar, then Metformin is used. With this treatment, hormonal levels are normalized, which allows the woman to conceive a child. At the discretion of the gynecologist, hormonal stimulation of ovulation or surgical intervention (laparoscopy) is performed.
The functioning of the ovaries is impaired for various reasons and can occur even against the background of intense and prolonged stress. Sometimes, to normalize the functioning of the reproductive system, it is enough to eliminate negative factors. Loading…
Source: https://kazandoctor.ru/ginekologiya/zabolevaniya/narushenie-raboty-yaichnikov-u-zhenshhin
Diagnosis and treatment of cysts
It is very important that a woman, when identifying the first signs of a developing cystic neoplasm, contact a specialist who will prescribe effective treatment. It is noteworthy that some types of cysts require simple observation.
There are criteria that indicate that a cyst should be removed. According to experienced doctors, a single-chamber formation with thin walls and a size of 10 cm without signs of growth will almost 70% not transform into life-threatening cancer.
Drug treatment
The tumor may gradually increase in size, but if it does not develop into a malignant formation and does not interfere with the normal functioning of internal organs, it can be eliminated using conservative therapy. After identifying the symptoms of ovarian cysts in women, treatment and prevention will be as follows.
If a papillary mucinous or serous cyst is detected in a woman of retirement age, surgery is indicated, since without proper treatment, ovarian cancer can develop. The use of certain medications makes it possible to reduce the formation in size and smooth out the symptoms as much as possible.
Typically, a doctor prescribes the following medications for the treatment of ovarian cysts in women over 50 years of age:
- Progestins or gestagens (Norkolut, Duphaston).
- Estrogen-containing drugs (“Marvelon”, “Ovidon”).
- Antiestrogens (Tamoxifen).
- Drugs to stimulate the immune system (Cycloferon, Timarin).
- Ascorbic acid.
- Anti-inflammatory suppositories with indomethacin.
- Analgesics (Baralgin).
- Homeopathic remedies that can improve hormonal levels (“Lycopodium”, “Bromium”, “Kalium”, “Apis”), especially if the patient’s ovarian tumor proceeds without any particular difficulties.
What is traditional medicine capable of?
Traditional medicine is based on the use of medicinal plants, mushrooms, tree bark, and bee products. Of these, those that have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, hemostatic and other properties relevant to the existing problem are selected.
In the treatment of ovarian dysfunction, folk remedies are used for ovarian dysfunction, such as decoctions and infusions of herbs, which are taken orally in courses and douched. Their action is aimed at:
- reduction of menstrual bleeding to normal volume;
- relieving symptoms of inflammation;
- normalization of the cycle and restoration of ovulation.
Traditional medicine recipes should be used after consultation with a doctor, so that the treatment is successful and does not bring additional negative changes in well-being. Treatment with folk remedies for ovarian dysfunction should be carried out in conjunction with the recommendations of the attending physician and verification of this diagnosis. Traditional methods of treating ovarian dysfunction can be combined with traditional methods and significantly improve well-being.
Surgical intervention
Usually, surgery for ovarian cysts after 60 years is performed when they become malignant. The appendages are completely removed using laparoscopy or laparotomy:
- Laparoscopy involves the low-traumatic removal of a small cyst through expansions in the abdominal cavity, into which a special gas is injected. The laparoscope allows you to see the field of activity as fully as possible on the screen. Next, the tumor is removed with special instruments, after which the hole is sutured with materials with absorbable properties.
- Laparotomy - if a woman develops a large cyst during menopause, it will be much more difficult to treat. This type of surgery is performed using the same laparoscope, but in this case the incisions will be larger, since the surgeon needs to remove some organs, including the uterus and its appendages in particularly severe cases.
The choice of a specific method of operation depends on the following reasons:
- the likelihood of further development of complications;
- the time period when the cystic formation appeared;
- type of cyst - single or multi-chamber;
- the severity of the ongoing process;
- neoplasm density;
- technical equipment of the office where the manipulation will be performed;
- localization and size of the cyst - cystadenoma is subject to mandatory excision;
- the presence of pathological accumulation of fluid in the abdominal area.
Prevention
It is worth noting that in our time, doctors have not found a specific method that would help prevent the occurrence of ovarian cysts. Therefore, there is no definite answer to the question of what to do with an ovarian cyst after 60 years to prevent it from occurring. But you can simply follow simple preventative measures:
- promptly identify and eliminate hormonal disorders, treat inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- undergo medical gynecological examinations;
- adhere to proper nutrition, eat foods rich in vitamin A and selenium;
- follow the regimen for using hormonal drugs;
- Avoid visiting the solarium and staying in the sun for long periods of time.
Ovarian cysts in women who have reached the age of 60 can be treated. The main thing is to contact a specialist in a timely manner and undergo regular examinations, strictly following the prescribed treatment regimen.
Whatever type of cyst a woman develops after 60 years of age, it should not be left without proper diagnosis, observation and treatment. The consequences of an ovarian cyst after 60 years, the treatment of which was discussed above, are quite dangerous. In addition, at such an old age there is a risk of the cyst developing into a malignant formation. Therefore, a woman during menopause needs to be regularly examined by a gynecologist and undergo an ultrasound. Early detection of the disease will give a chance to completely get rid of its manifestations.
I was operated on, hot flashes started, but the ovary was left behind, I’ve been crying since 04/04, menopause? I want to cut my hair right now, take it and cut it off. DR was also 18/06, 40 years old, everything was an old woman, right now she was crying so much, her husband went to his mother - at first, when she returned from the hospital, he said some words, and now I’m howling in the kitchen, he smoked, got ready and left. They promised that everything would be fine, on 04/06/16 the operation was performed, the fibroid was removed within 9 weeks, but at first they said that embolization could be done. After the operation, she told her husband: “I saved my ovaries and vagina.” Then I read that the appendages on the left were removed, the ovary on the right was truncated. My neck was cut off, I am disabled. Then, as the surgeon said at home, they didn’t tighten the vessel - my seam was oozing with ichor and didn’t heal. In the examination room! They stitched me up - anesthesia again, stitched me up as shamefully as a dog. I was there for another 2 weeks; the seam on the left side did not heal; at Easter they sent me home with stitches (100 km). They said, if you come, we’ll rent it. At home, my husband saw the seam for the first time when he was greasing it. Then we went to the local surgeon, he said: Yes, your threads have already come apart, you need to cut them off. I put a rubber band on the hole on the left, it took another month to heal, I didn’t write anything, what if I had adhesions - after all, it was bleeding inside? and the adhesions grow from this. Then just on June 17 (2 months) a hole in the middle became overgrown, it was so round, it was terrible. This is when it passed on the left and formed in the middle. Levomikol seemed to help. And on 01/06 I went to our gynecologists - fever at 5.00 in the morning, my heart was jumping out: what I thought was menopause. Have you been prescribed AEvit, MagnesiumB6, Klimadinon hormones? I refused. I suffered until June 17, but went again. And also because of mild mastopathy on the left side, I first went to see a mammologist. He says that there is something mild, but it’s okay, if you want, come for an ultrasound after Trinity. And, having learned about the operation and hot flashes, he offered to buy it for 1100 rubles. “Women’s Health” some Russian dietary supplement.vitamins, He says there are a lot of tablets there. I read that you need to drink herbs, since they stuffed it all into this 1 tablet. Did not buy. A gynecologist, not interested in anything - but you need to get tested, predispose. to cancer. etc. (as they write), attributed to hormones. Sedatives and take a test for FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone.) I came - I read - the brain does not secrete it, and the cell and estrogen do not mature in the ovary. I'M GOING CRAZY, EVERYTHING HAS COLLAPSE. And I’m also overweight, last year I ran with this fibroid, and I pumped my abs - in the school yard - it’s useless, I shook the film while running - I almost died, and my hemoglobin was terrible, as it turned out in October, and that I have myoma. WHERE DID SHE COME FROM? Of course, I cried a lot - mom in 1999 at 46 years old, dad in 2013 at 65 years old, missed cancer - although I was seen by a doctor every week, hemodialysis, grandmother in the arms of 2020, everyone died. Did I make her cry? and also my husband - don’t touch him, and don’t. And now he doesn’t bother me. And he is 37. This infuriates me, and before this it happened 3 times. per month, and that’s only good for him. I also read that there will be dryness of the moisture, there is no estrogen, and desire will decrease; testosterone also depends on estrogen. A husband against hormones will make you even more angry. I’ve seen people like that! My legs are swollen, my arms too. In the hospital I lost weight while I was there for 25 days on porridge. At home I gained weight again. Now my whole head is wet, my heart is jumping out. What to drink for rapid heartbeat? The breasts sagged. The seam. If you pass along it, it’s like the strings on a harp - transverse figs under the skin. Gynek. she looked and said, Well, what do you want? There is not even a normal seam (and I paid 10,000 UAH). Let the laser do the ride? I don't have money for it. Isn't it their fault? I heard out of the corner of my ear what the doctor was saying - Come, I’ll give you a laser! And I'm worse. They think I’m not coming, so everything is fine with me? Far from simple! Gasoline will go away((( FLASHES SUCH HUSBAND SWELLING HEART PRESSURE (I’ve been drinking clover for the 2nd day) I really want a tummy tuck Oh, and the seam is cut, now the stomach hangs over it, you can’t reach the seam, you have to raise your stomach like that, I didn’t have that, there's a seam inside somehow, every day I think about suicide. If it weren't for my daughter, they would have ruined me. Memories come flooding back, I see everything so clearly, how I buried everyone, and why live. I'm ugly. Even if I get enough for plastic surgery, I'll have to stitch up my stomach ", I'm afraid that there is a blood clot or complications, or I won't be able to stand it - this is not a solution. So, there is no hope, I will remain like this. Legs - maybe some kind of massage? I'm swollen, swelling. And there in the hospital, when I complained to them, I thought Oh, I got to the professors - they will cure everything. They said that due to adipose tissue my blood vessels are compressed - that’s why I have swelling. Lose weight! And when I was running, I was so out of breath. 200m and I’m dying, from April 15 to October 15, of course, something went away, but shortness of breath. how do these fat men run 40 km on TV? what’s wrong with me? they checked my heart, there’s something wrong with the ventricle. I was also pregnant when I was vomiting since I was 4 months old. and after heartburn there was another 3 years, and until October 15, when the general practitioner said Drink Omeprazole! And it seems to have cured me. You still have to swallow the hose, sometimes it gets hot. It’s easier to die, they won’t cure anything. Let's go buy flip flops - it's already 41 sizes, and what's beautiful and you can't buy it is just a woman's thing. And I didn’t buy a T-shirt. They chose a striped dress for me, like the old women's. And I was so skinny. The left arm also becomes numb and goes numb, as if you lay down. And sitting on your tailbone hurts when you get up. It’s impossible to get up, I thought they’ll cut out the fibroid and it’ll go away. MRI alone costs 1800 rubles, I won’t go.
What is ovarian failure syndrome and how is it treated?
Dysfunction of hormone-producing organs, complicated heredity, infectious diseases and surgery are recognized as the main causes of early menopause, a clear manifestation of which is ovarian depletion. Treatment of this pathology is based on the use of synthetic hormones, phytocomplexes and physiotherapy aimed at restoring fertility and eliminating the unpleasant symptoms of menopause.
Factors that provoke ovarian depletion
Exhausted ovarian syndrome is diagnosed in 2% of women of late reproductive age (35-45 years), in whose bodies the maturation of follicles and the synthesis of sex hormones stops.
The development of a pathological process in young women is also possible.
Even at the time of intrauterine development, a certain number of primordial follicles are formed in the female body, which are activated only during puberty under the influence of hypothalamic hormones.
With each menstrual cycle, the follicular reserve gradually decreases. Complete loss of ovarian function, as a rule, occurs after 50 years and indicates a woman’s further inability to reproduce.
This is menopause - a natural physiological process that cannot be avoided. However, there are situations when depletion of the follicular apparatus occurs ahead of schedule: the ovaries stop synthesizing their own hormones.
Depletion of the follicular reserve is most often caused by a genetic factor, the so-called 3-chromosome syndrome, which appears under the influence of gene mutations in the prenatal period of embryo development. The abnormal structure of the ovaries leads to their premature aging.
An equally popular theory for premature decline in ovarian reserve is hormonal dysfunction. Increased production of gonadotropins triggers a mechanism of damage to the reproductive system, when autoimmune antibodies destroy the ovarian tissue's own tissue, reducing the supply of full-fledged follicles.
The decline of ovarian function earlier than the age norm can also be caused by other reasons:
- infectious diseases;
- chronic diseases of the endocrine, nervous, excretory systems;
- surgical intervention in the reproductive organs (resection of the ovaries, removal of cysts, tumors);
- intoxication of the body with drugs and toxic substances;
- diseases suffered by a woman during pregnancy;
- stressful situations;
- high physical and mental stress;
- strict diets, fasting;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body;
- autoimmune diseases;
- negative impact of ionizing radiation.
When is treatment needed?
Ovarian wasting syndrome has characteristic symptoms: external age-related changes and an abnormal structure of the paired organ, diagnosed during its examination.
The following signs may indicate lazy (depleted) ovaries:
- lack of ovulation despite regular sex life without the use of contraceptives;
- hot flashes;
- increased sweating;
- dizziness, headaches;
- cardiopalmus;
- blood pressure surges;
- swelling of the limbs;
- darkening of the eyes when changing body position;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- decreased physical activity;
- memory impairment;
- hair loss, thinning of hair;
- changes in the structure of skin, hair, nails;
- the appearance of wrinkles on the face and neck;
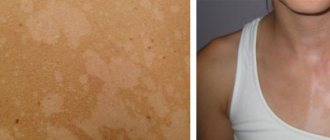
- hyperpigmentation of certain areas of the skin;
- psycho-emotional instability;
- male pattern fat deposition;
- underdevelopment of secondary sexual characteristics;
- frequent, unproductive urination;
- vaginal dryness;
- decreased sex drive;
- the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases.
A laboratory blood test indicates ovarian depletion:
- low levels of estrogen, progesterone, estradiol, prolactin, prostaglandins;
- high concentration of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, triglycerides.
Signs of ovarian depletion (aging) can also be confirmed using instrumental diagnostics:
- Electroencephalography determines brain activity, reveals dysfunction of the hypothalamus, and the presence of diseases of the central nervous system that affect the functioning of the ovaries.
- Using metrosalpingography, you can detect a decrease in the size of the uterine body, narrowing of its cervix, and thinning of the endometrium.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs determines the reduction of the ovaries, underdevelopment of the follicular reserve, the absence of maturing follicles, and the presence of any neoplasms.
- Laparoscopy of the ovaries followed by a biopsy is aimed at examining the connective tissue, outer layer, and structure of the organ. As a result of a cytological examination, the replacement of ovarian tissue with connective tissue and the absence of full-fledged follicles are confirmed.
Depleted ovaries and pregnancy
Is it possible to get pregnant with depleted ovaries? There is a chance for successful conception provided that timely treatment with hormonal drugs is provided. Exhausted ovarian syndrome is not a death sentence at all. Pregnancy occurs in 60% of cases if the provoking factor is eliminated.
However, it is necessary to remember that against the background of depleted ovaries, the risk of gestational diabetes, hypertension, preeclampsia, and weight gain increases.
The presence of this pathology also affects the intrauterine development of the fetus, provokes miscarriage, and premature onset of labor.
The goal of hormone therapy is to stimulate ovulation:
- First of all, the attending physician prescribes antiestrogenic drugs that help restore the natural menstrual cycle.
- For infertility of progesterone origin and habitual miscarriage, Duphaston is used for 3-6 months. For amenorrhea, Duphaston is used in combination with estrogens from the 11th to the 25th day of the menstrual cycle for 3 months. The same treatment regimen is followed for the short luteal phase.
- In the absence of a positive result of treatment, follicle-stimulating hormone drugs (Metrodin, Urofollitropin) are indicated to achieve “superovulation”. The drug is taken for 2 or more menstrual cycles in consultation with the attending physician. To stimulate the growth of multiple follicles, the doctor may prescribe assisted reproductive techniques.
If, as a result of conservative treatment, pregnancy does not occur, surgical intervention using laparoscopy is resorted to. Wedge resection of the ovaries involves removing 2/3 of the organ. Medical statistics confirm the effectiveness of such treatment in most cases.
Hormonal therapy carried out in pregnant women involves the use of drugs that cause normal secretory transformations in the endometrium, contributing to the successful gestation of the fetus. From 11 to 25 days of the menstrual cycle, Duphaston is prescribed, adjusting the dose after colpocytological examination.
Hormonal therapy is contraindicated during the lactation period, as it passes into breast milk. Breastfeeding is stopped during treatment.
Traditional medicine
Traditional methods of treatment are included in complex therapy, but do not replace the classical treatment regimen for ovarian dysfunction.
- Exhausted ovarian syndrome is treated with sedatives and infusions. A positive effect on the nervous system was noted from infusions of peppermint (1 tablespoon of dry raw materials per 0.5 liters of water), viburnum, cranberry and blackberry fruit drinks.
- Eliminates psycho-emotional instability freshly squeezed beet juice (100 ml), to which 1 tbsp is added. l. honey The medicine is taken 2 times a day, 50 ml.
- Treatment with folk remedies includes the use of egg-lemon suspension, which effectively combats the manifestations of early menopause due to its high lecithin content. To prepare it, you need to grind lemons and eggshells using a blender in a 1:1 ratio. The resulting mixture is infused for 3-4 weeks, and then consumed 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. spoon.
- You can eliminate the symptoms of ovarian depletion with the help of an infusion of boron uterus. Brew 1 tbsp in 250 ml of water. spoon of dry herb and leave for 30-40 minutes. The infusion is taken up to 5 times a day, 1 tbsp. spoon before eating.
- Infusions of wintergreen, one-sided ortilia, red brush, and field grass, which are prepared in a similar way, have similar properties.
- When the ovaries are depleted, the daily diet must include foods containing lecithin, folic acid, natural phytoestrogens, and B vitamins. These include sprouted grains of wheat, rye, soy, lentils, beans, cauliflower, nuts, fish, egg yolks and others.
- To prepare herbal tea with phytoestrogenic properties, clover, alfalfa, viburnum, sage, ginger, and Abraham tree are used. 0.5 tsp. dry raw materials are brewed in 250 ml of water and left for 15-20 minutes. Take 2-3 times a day for two to three weeks.
Traditional medicine is used only after consultation with the attending physician. Any plant is a potential allergen and, if the body is sensitive, can produce the opposite effect.
Timely identification of the true cause of early depletion of follicular reserves and an integrated approach to treatment prevent loss of fertility and unpleasant symptoms of early menopause.
Source: https://DrLady.ru/disease/chto-takoe-sindrom-istoshhennyh-jaichnikov-i-kak.html
What is a “dormant ovary”
The term “dormant ovaries” is not used in official medicine. This is a generally accepted colloquial form that refers to a woman’s health condition due to ovarian dysfunction.
This concept replaces the medical names - ovarian dysfunction, premature menopause, premature ovarian failure.
Most infertile women face this problem. To understand how to wake up the “sleeping ovary,” doctors prescribe a series of tests and examinations.
Only after finding out the cause can you begin to treat the pathology. When dysfunction of the gonads occurs over the age of forty-five years, this may be a sign of the onset of menopause.
Irritability is one of the signs of ovarian dysfunction
OVARIAN REJUVENATION THERAPY (PRP)
We change the biological clock of women suffering from infertility and premature menopause
Stem cells, under certain biological influences, change into any type of cell in the human body, including eggs. The presence of such cells in the ovaries and their transformation into mature eggs was proven in experiments on mice by scientists from Harvard.
It was also discovered that stem cells exist in human ovaries, which makes it possible to transform them into eggs with the help of growth stimulants that are contained in the leukocytes and platelets of women. Extracts of growth stimulants have long been used in medicine, in its various directions, they consist of the blood and cells of the patient himself and are called PRP (platelet-rich plasma) or PDGF (platelet growth stimulator)
What are growth promoters, how do they work and are they safe?
Growth promoters are naturally produced from certain blood cells (platelets and white blood cells) to naturally heal a person when they are injured. Remember, as a child, some abrasions on your knee would produce a yellow, thick fluid. It is actually a combination of platelets, white blood cells, blood coagulation (blood clotting) and growth promoters that: stop bleeding, prevent infection, and ultimately lead to the formation of new skin, blood vessels, connective tissue and nerves to replace those who were lost or injured.
These PRP extracts have been used in medicine for many years by doctors to treat soft and connective tissue injuries, as well as bone tissue transplants. Many professional athletes use this treatment to speed up the healing of injuries. PRP extracts are also used for skin regeneration in burn patients, and even in non-surgical facelifts. Of course, there are studies that confirm or refute the effectiveness of PRP treatment in a variety of medical applications. However, PRP therapy is undoubtedly safe, given that the patient’s own blood cannot be a carrier of viruses: HIV, hepatitis, etc., as could happen with the use of stimulants from the blood of other people. In addition, since there are no synthetic or chemical substances involved in PRP therapy (from the patient's own blood), the likelihood of an allergic reaction is extremely low.
How does the process of ovarian rejuvenation occur?
The process of ovarian rejuvenation includes two stages. Initially, a PRP hood is done. This procedure begins with a fairly large amount of blood being drawn from you. All white blood cells and platelets are separated from the red blood cells and serum in a process called centrifugation. This process lasts less than an hour, the next part of the procedure is injection of the drug into the ovaries. The main uniqueness in our study and the method described in this case is that the technique we developed for injection into the ovaries is not a surgical procedure. It occurs under anesthesia and also includes transvaginal ultrasound - which guides the injection. This is the same process as egg retrieval during IVF. Based on our experience, this procedure is less invasive and safer.
We have performed thousands of IVF with egg recovery over the last 25 years with a very low complication rate.
What are the possible risks and what are the benefits of this procedure?
The advantage of this process is the possibility of pregnancy with the woman's own egg, which was not possible before this procedure. You should understand that this is an innovative development and there are no guarantees, express or implied, that pregnancy will be possible, either naturally or as a result of any subsequent procedures. The risks of this procedure are minimal, they are the same as in the process of egg retrieval, which is part of IVF.
Side effects include possible pain after surgery, which usually goes away within 1-2 hours with the help of pain medication. Complications are rare.
Who are the candidates for this procedure?
Every healthy woman belongs to one or more of the following four patient categories:
- Women under 50 years of age who are premenopausal or menopausal
- Infertile women over 35 with low egg reserve and low hormone levels (AntiMullerian-AMH)
Women under 35 years of age with low egg reserves and low hormone levels (ΑΜΗ)
- Women with premature ovarian failure (POF)
How does the process of ovarian regeneration occur?
For women who do not have a menstrual cycle, the procedure can be performed at any time. And for women with a normal or irregular cycle, it is advisable to start the procedure at the beginning of the cycle, before the follicles begin to mature.
The results of ovarian rejuvenation are successfully monitored through hormones (FSH, LH, AMH and estradiol) monthly in a woman without menstruation and for 6 months in women with a normal or irregular menstrual cycle. If ΑΜH levels increase, while FSH, LH and estradiol levels decrease, then these are objective signs that prove ovarian rejuvenation. Even if rejuvenation is observed, pregnancy will not necessarily occur, because There may be other factors that interfere with natural conception.
It is also possible to introduce a drug extract (PRP) to thicken the endometrium and implant embryos in cases of unsuccessful IVF attempts or repeated miscarriages. Of course, more tests and studies are needed to confirm the effectiveness of this method in a larger number of women.
Results and Gratitude
Every day we use PRP therapy to rejuvenate the ovaries in our center with success. You can find words of support and gratitude on pages No. 1 and No. 2.
This fact prompted us to use the PRP procedure in other cases:
- vaginal atrophy
- aesthetic treatment of vagina and lips
- some cases of urinary incontinence,
since PRP helps regenerate healthy tissue. US Expert References Describe increased genital sensitivity that leads to a more emotional and pleasurable sexual experience.
“Crete Fertility Center ” offers you all available treatment methods to achieve a holistic therapeutic approach.
Fraidakis M. D.
Related articles: Vaginal Rejuvenation