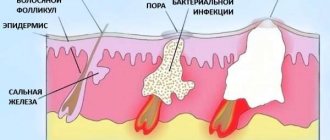
Main reasons
Problematic skin is a very common phenomenon among people of various age categories. Pimples and blackheads can occur in both men and women. Pimples that appear on the face vary in appearance, origin and other factors.
The formation of a pathological compaction occurs gradually, and the duration of pimple maturation can last for several weeks. And during its formation, an infection usually occurs, promoting inflammation. This whole process causes great discomfort, since subcutaneous acne is very painful.
In order to eliminate the disease in question, it is necessary to establish the most precise causes that contribute to the appearance of these inflammatory elements.
The main problem here is the overactive activity of the sebaceous glands, which results in clogging of the pores and sebaceous ducts. Such conditions are very favorable for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, which provoke the occurrence of the inflammatory process.
Internal acne can appear not only due to some external factors (improper or insufficient facial care), but also due to various diseases of the organs and systems of the human body.
Therefore, consideration of this pathology must be approached comprehensively. Here there is a need to find out why the sebaceous glands do not work correctly, contributing to the development of the inflammatory process. And for what reason the epidermis cannot cope with pathogenic microbes and the skin’s immunity is weakened.
The main reasons for the formation of subcutaneous acne:
- increased secretion of the sebaceous glands;
- insufficient or improper facial care, which results in expansion and clogging of pores and ducts in the epidermis;
- use of cosmetics that do not match your skin type;
- serious changes in the body's hormonal system, which are usually observed in adolescents, pregnant women, before the onset of menstruation, during menopause;
- demodicosis or subcutaneous mite is a serious dermatological disease characterized by multiple formation of ulcers and internal inflammatory elements;
- the use of low-quality cosmetics that contain components that have an adverse effect on the epidermis, contributing to the development of inflammation on the face of various types;
- poor hygiene, careless attitude to facial cleansing;
- excessive cleansing of the face, the use of soap or other products that dry the skin, as a result of which the protective layer on the surface of the epidermis is destroyed, which protects against the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms;
- habit of touching your face with your hands;
- Self-squeezing pimples and blackheads often provokes a worsening of the situation.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is the body's response to pathogenic stimuli or negative physical impact. In other words, inflammation is one of the body’s defense mechanisms.
One of the main manifestations of the inflammatory process is redness of certain areas of the body, the appearance of swelling, pain, fever and other similar symptoms.
In many sources, the inflammatory process is characterized by “hellish sensations,” in particular through the above-mentioned symptoms. However, when the inflammatory process becomes chronic, the affected area of the body becomes cold to the touch and the swelling goes away.
In this article, we will focus on the stage of the inflammatory process when the body becomes red and the affected area is swollen, painful, and feels hot to the touch.
When and how should you use medications to reduce inflammation?
- Immediately after injury, if there is no open wound on the body
- Any area of the body that suffers from chronic pain (particularly the back and joints)
- On the neck, especially after suffering from infectious diseases of the throat
- In the area near the liver (to the right of the chest), if you are worried about pain or hyperemia. In this case, we recommend using ice therapy, and two methods that we will describe below.
- Around the abdomen, especially if you suffer from bloating or other stomach problems.
Red pimples and blackheads
In addition to subcutaneous ones, other pimples, for example red ones, may appear on the face. They cause no less discomfort, since they greatly spoil a person’s appearance, and sometimes cause disgust.
Red acne tends to spread all over the face, covering the cheeks and chin, nose and forehead. At the same time, it is almost impossible to hide such inflammatory elements with foundation. On the contrary, in this way the condition of the dermis will only worsen. It is important to find the cause that can lead to such a problem, and by eliminating it, you can enjoy clean and healthy facial skin.
The causes of redheads and pimples are hormonal imbalances, poor nutrition, parasitism, dysbacteriosis, improper facial skin care, subcutaneous mites, etc.
Teenagers often suffer from this pathology due to hormonal changes in the body. But if you do not carry out appropriate treatment and do not take proper care of your face, the skin thickens, cysts and congestion form on it. As a result, the complexion becomes bluish and unhealthy. It is required to undergo a series of examinations by a dermatologist to exclude the presence of chronic diseases and undergo a course of treatment.
Ice compresses
In this article, we have already mentioned that burning pain is one of the main symptoms of the inflammatory process, therefore, to eliminate such pain, we recommend using one of the oldest and simplest remedies - ice.
Remember that ice should not be applied to a naked body, but you can use the following methods of ice therapy:
- Bag of frozen vegetables or fruits
- A handful of ice cubes wrapped in a cloth
- Special compress with ice
Apply ice to the affected area for at least 20 minutes.
When the inflammation becomes chronic, the body no longer feels hot to the touch, and the affected area may even become colder than the rest of the body. In this case, it is better to reduce the inflammatory process with the help of warm compresses (heating pads, bottles of warm water, etc.).
Lumps on the face that are not related to acne
Acne is a fairly common and studied phenomenon that affects a large number of people of different ages. But in some cases, certain formations appear on the face that are not at all similar to ordinary pimples or acne. These lumps or cysts are called wen, and they are usually not painful or cause discomfort.
It is not recommended to remove wen from the skin on your own, as this can lead to deterioration of the epidermis and the formation of other, more serious skin growths.
The main reason for the appearance of such tubercles is the enlargement of the sebaceous glands themselves. Wen differ from pimples in color (they blend in with the skin color or are white), as well as in the absence of inflammation and redness.
You can get rid of wen with the help of some professional cosmetic procedures:
- mechanical cleaning;
- deep peeling;
- laser removal;
- electric shock.
DEFINING ACNE.
Suddenly feeling like a teenager and struggling with acne again? You shouldn’t blame it on the bad environment, the dessert you ate, or the lack of intimacy with your loved one... Most likely, you are faced with an acne problem, which should be dealt with immediately. This is an inflammation of the sebaceous gland of a certain localization: on the face, back, neck, décolleté, less often on the buttocks and shoulders). Typically, this disease is long-term in nature (lasts months, or even years), sometimes exacerbating (the number of inflammatory elements increases), sometimes going into a state of remission. Clinically manifested by “greasy” facial skin, the presence of comedones (“blackheads”), purulent inflammation and pigmentation.
Reducing chronic inflammation will protect you from many diseases and prolong life
Many people believe that inflammation is a local nuisance, for example, when you get a cut finger, a sore throat or a toothache. In reality, inflammation spreads throughout the body.
Acute inflammation is quite transient. It performs its functions, for example, fights infection and ends.
If inflammation lasts for a long time, healthy cells begin to suffer from it. Inflammation is not always infectious.
Chronic inflammation may be caused by the body's inability to eliminate an acute inflammatory factor, an autoimmune response to a self-antigen, or may be caused by a persistent low-intensity chronic irritant.
For example, it can occur due to obesity or overweight. In this case, the inflammation is quite weak, but at the same time extremely long-lasting!
Many common and clinically significant disease conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, tuberculosis, leprosy, chronic hepatitis, thyroiditis and multiple sclerosis, are examples of chronic inflammation and its consequences.
Inflammation also contributes to the development of other diseases that are not defined as inflammatory.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228018154_Inflammation_Chronic
Inflammatory diseases account for half of all deaths worldwide.
Prevention, early diagnosis and treatment of chronic inflammation will reduce the risk of chronic disease and death.
Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system that helps fight disease and infection. However, chronic inflammation increases the risk of developing potentially fatal diseases.
Chronic inflammation plays a key role in heart disease, cancer, diabetes, kidney disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders.
Chronic inflammation is influenced by many social, environmental and life factors.
Risk factors for chronic inflammation include: obesity, physical inactivity (lack of exercise or physical activity), social isolation, chronic stress, and insufficient or poor sleep.
The presence of inflammation can be determined by several biomarkers, primarily by increased levels of C-reactive protein in the blood plasma.
C-reactive protein helps neutralize and destroy various infectious agents, and also stimulates the development of an inflammatory response as a defense mechanism for the body.
C-reactive protein binds to specific molecules, in particular proteins on the surface of the bacterial cell, which are released from tissues damaged by bacterial toxins.
There is always some small amount of C-reactive protein in the blood. The liver is its main supplier. In addition, the protein can be produced by the epithelium, or inner surface of blood vessels.
Bacterial and viral infections, trauma, surgery, tumors and other factors can increase CRP levels many times over.
The C-reactive protein marker indicates a pathological process in the body, without indicating its cause or location.
The normal level of CRP should be less than 10 mg/l.
Inflammation is a contributing factor not only to physical health problems, but also to mental health problems such as anxiety disorders, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, schizophrenia, self-harm and suicide.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-019-0675-0
There are several risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing and maintaining a low-grade inflammatory response:
Age
Unlike younger people (in whom levels of inflammatory cytokines typically increase only in response to infection or injury), older people may have consistently elevated levels of inflammation. These elevated levels are observed even in healthy older adults.
Although the reasons for this age-related increase in inflammatory markers are not fully understood, it may reflect cumulative mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage or may be the result of other age-related risk factors (such as increased visceral body fat or decreased sex hormone levels).
Read more about this in the article “Inflammation in Aging.”
Overweight and Obesity
Adipose tissue is an endocrine organ that stores and releases many hormones and cytokines into the bloodstream and influences metabolism throughout the body.
Fat cells produce and release the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor) and interleukin IL-6, and visceral (abdominal) fat can produce these inflammatory molecules at levels sufficient to cause a strong inflammatory response.
Nutrition
General over-consumption of food is a major contributor to inflammation.
Calorie restriction provides powerful protection against inflammation. A diet high in saturated fat is associated with higher pro-inflammatory markers, especially in diabetics or overweight people.
Low levels of sex hormones
Testosterone and estrogen can suppress the production and secretion of several proinflammatory markers.
Normal levels of sex hormones are associated with a reduced risk of developing a number of inflammatory diseases, including atherosclerosis, asthma in women and rheumatoid arthritis in men.
Hormone replacement therapy may exert its protective effect in part by reducing the inflammatory response.
Smoking
Cigarette smoke contains several inflammatory inducers, particularly reactive oxygen species.
Smoking increases the production of proinflammatory cytokines and also increases the risk of developing periodontal disease, an independent risk factor for increased systemic inflammation.
Insomnia
The production of inflammatory cytokines appears to follow a circadian rhythm and may be involved in the regulation of sleep in animals and humans.
Disruption of normal sleep can lead to daytime increases in levels of these pro-inflammatory molecules.
Other provoking factors
Periodontitis can cause a systemic inflammatory response, which in turn can affect various organs and systems.
Periodontal disease is believed to be a risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Stress can lead to the release of inflammatory cytokines.
It is also associated with poor sleep and weight gain (stimulated by the release of the stress hormone cortisol), both independent causes of inflammation.
Healthy lifestyle and nutrition to reduce chronic inflammation
Inflammation itself is not a disease, but to one degree or another it has an adverse effect on health.
Because adipose tissue (especially abdominal fat) expresses inflammatory cytokines, obesity may be a major cause of low-grade systemic inflammation.
Therefore, it is very important that the total energy intake is proportional to the energy expenditure to avoid the deposition of abdominal fat.
Energy expenditure through exercise reduces multiple cytokines and proinflammatory molecules independent of weight loss.
Although muscle contraction during exercise initially results in a pro-inflammatory state, it paradoxically reduces inflammation!
This effect is observed in everyone - both healthy and sick in all age groups.
https://jlb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1189/jlb.0505247 https://journals.lww.com/acsm-msse/Pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2012&issue=06000&article=00015&type=Fulltext
As mentioned above, restricting incoming calories, combined with high physical activity, allows you to maintain optimal energy balance and helps counteract chronic inflammation.
The qualitative composition of consumed fats (trans fats, oils with a poor fatty acid composition, etc.) and carbohydrates (fast carbohydrates, fructose) can have a significant impact on the progression of inflammation (as reflected by an increase in the content of pro-inflammatory markers). While omega-3 polyunsaturated fats appear to be anti-inflammatory.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/226114519_Omega-3_Polyunsaturated_Fatty_Acids_and_Health
Excess glucose in the blood triggers inflammatory processes.
Diets with a high glycemic load are associated with increased proinflammatory markers and an increased risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes, especially among overweight individuals.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0884533610385703 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18249220 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ 18326604
When glucose is used correctly, our cells produce energy efficiently. As cellular sensitivity to insulin decreases, excess glucose accumulates in the bloodstream.
Like spilled gasoline, excess glucose in the blood creates a “fire hazard” environment in which oxidative and inflammatory fires constantly occur.
Excess glucose not used for energy is converted to triglycerides, which are either stored as unwanted fat deposits or accumulate in the blood, where they contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
That is why it is important to have constant physical activity, not to overeat and, if possible, exclude sugar, sweets, fast carbohydrates and foods with a high glycemic index from your diet.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15306213 https://nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1196/annals.1333.052 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/ article/pii/S0006291X09020440
Fiber (dietary fiber)
Fiber intake (vegetables, bran, whole grains) correlates with significant reductions in inflammatory markers.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2603616/ https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/01/190110184737.htm
Micronutrients to Reduce Chronic Inflammation
Magnesium
Magnesium intake is associated with lower levels of inflammation. Research has found a significant association between higher dietary magnesium levels and lower levels of homocysteine and fibrinogen, proteins associated with inflammation.
Magnesium was rated as the most anti-inflammatory dietary factor in the Dietary Inflammatory Index.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2777480/ https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/2/304 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov /pubmed/24290571
Vitamin D
Vitamin D exerts anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing pro-inflammatory prostaglandins and inhibiting inflammatory mediators.
Vitamin D deficiency can contribute to inflammation. Vitamin D deficiency is more common among patients with inflammatory diseases (including rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, and diabetes) than in healthy people.
Deficiencies of this vitamin are also more common in populations prone to low-grade inflammation, such as obese people and the elderly.
https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/6/4/e010804 https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0141770
Other drugs to reduce chronic inflammation
Glucosamine
Glucosamine Sulfate inhibits the central inflammatory mediator NF-kB.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25719429
Low dose statin
Statins are thought to reduce inflammation by a mechanism distinct from their effect on cholesterol metabolism. They interfere with the function of cytokine receptors on the surface of leukocytes. Therefore, pro-inflammatory signals in the blood are unable to provoke a response from leukocytes, and they are prevented from further stimulating inflammation.
Rosuvastatin is the most effective. It also has a minimum of adverse side effects.
The dosage and duration of use should be determined by a specialist.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6740083/ https://insights.ovid.com/crossref?an=00041433-201106000-00004 https://link.springer.com/article /10.1007%2Fs11883-009-0037-3
You can buy drugs to reduce chronic inflammation by clicking on the name:
Glucosamine Vitamin D Magnesium Omega-3
Detailed instructions on how to place an order and receive it >>> HERE .
If the link to the drug does not open and the site does not load, how to correct the situation is described in the article “How to access the IHerb website if it does not load?”
I also recommend reading:
Vitamin D and Brain Health Vitamin D Science-Based Health Benefits Vitamin D for Multiple Sclerosis Vitamin D Increases Human Lifespan Aging Inflammation Glucosamine Slows Aging and Increases Lifespan Glucosamine Anti-Aging Skin Glucosamine Reduces Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Move more, live longer! Magnesium deficiency and its impact on quality and life expectancy Magnesium optimizes vitamin D levels Magnesium reduces mortality Low on energy? Perhaps there is not enough Magnesium in the body!