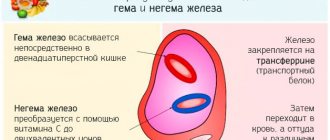
Reduced hemoglobin: reasons
The human body loses iron-containing protein for a number of reasons. The most common are the following:
- Blood loss, which is divided into: obvious, i.e., visible loss of blood by the body due to abdominal operations, wounds, serious injuries, advanced hemorrhoids, heavy menstruation in women; hidden – the development of internal bleeding with the progression of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Low content of vitamins and amino acids, which are necessary for the process of hemoglobin synthesis. If the body does not have enough vitamin C or folic acid, this is due to an unbalanced, poor diet.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency, which is possible due to helminthic infestation.
- Problems with the digestive system: gastritis, colitis, ulcers. These ailments interfere with the absorption of iron, due to the depletion of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Infectious diseases of a severe nature: hepatitis, tuberculosis, etc. The pathological processes that accompany these diseases lead to the premature death of red cells in the blood. As a result, a person's hemoglobin may drop below 50 g/l.
- Hypothyroidism is a severe syndrome that is caused by decreased levels of hormones in the thyroid gland. It is hormones that regulate the absorption of iron in the intestines; accordingly, when they are deficient, hemoglobin decreases.
- Autoimmune diseases that lead to damage and destruction of normal tissues.
- A malignant blood disease causes hemoglobin levels up to 50 g/l.
- The presence of neoplasms in internal organs.
- The presence in life of stressful situations that, depressing the psyche, can make a person feel depressed. Negative emotions disrupt metabolic processes, affecting a decrease in hemoglobin.
- Imbalance in nutrition. Harm can occur not only due to insufficient intake of necessary beneficial elements and substances into the body. There are also a number of products that, when consumed in large quantities, can cause a decrease in hemoglobin. These include: strong coffee, tea, chocolate, cereals. All these products inhibit the absorption of iron.
- Low physical activity, which can serve as a catalyst in slowing down the movement of blood through arteries, veins and capillaries. At this moment, the human brain receives a signal that says that there are enough red blood cells in the body, so there is no need to produce them.
A natural reason for a low level of iron-containing protein is constant donation. If the person is healthy, then in this case everything will quickly recover, but if the hemoglobin does not return to normal, then the medical staff refuses the services of this donor.
The main causes of low hemoglobin in the blood
Let's take a closer look at the causes of low hemoglobin and how to deal with them in order to feel healthy and full of energy!!!
Main function of hemoglobin
Iron's main function in the body is to bind proteins to produce hemoglobin, a special protein that gives red blood cells their color.
Hemoglobin is needed to carry oxygen through the blood from the lungs to the tissues of the body, to form myoglobin, which is necessary to carry oxygen to our muscles, and to carry carbon dioxide away from cells and deliver it to the lungs.
Normal hemoglobin level in human blood
The normal concentration of hemoglobin in the blood is 13.5 to 18 g/dl in men and from 12 to 16 g/dl in women.
Why is hemoglobin low?
The main reasons for a decrease in hemoglobin levels in the blood may be the following:
- Insufficient iron content in food consumed.
- Abnormal absorption of iron in the stomach and small intestine.
- Lack of animal protein in food.
- Of particular importance is the content of vitamin B12 and folic acid, which are also absorbed in the upper gastrointestinal tract and are directly important for the formation of red blood cells in the human bone marrow.
- With a decrease in the number of red blood cells, the amount of hemoglobin per liter of blood decreases accordingly.
- Pathological processes in the body, bleeding, diseases of the hematopoietic system, pregnancy.
- Excessive blood loss, for example, with severe nasal, gastric and uterine bleeding or with frequent donation.
- Anemia
Symptoms of the disease
A decrease in hemoglobin to 50 g/l has the following symptoms:
- Subjective – it is evidenced by the patient’s complaints.
- Objective, which is measured quantitatively.
Subjective asthenic symptoms include:
- insomnia at night along with drowsiness during the day;
- weakness throughout the body;
- heavy morning rise, in which a person requires effort to get up;
- noise in ears;
- increased fatigue;
- frequent migraines;
- dizziness, sometimes fainting and fainting;
- menstrual irregularities;
- decreased appetite, up to complete aversion to food;
- decrease in potency.
All these symptoms appear due to a lack of oxygen in the tissues, and as a result, disturbances in the pH level of the cells occur.
Subjective dystrophic symptoms
You can also identify subjective dystrophic symptoms, which are signs of iron deficiency and are indirect in nature:
- the nail plates are affected: they delaminate, become thinner, break, and stains and fungal diseases may appear;
- hair deteriorates: it falls out, hardly grows, splits, becomes faded and brittle.
- disturbance of taste and smell, a desire may also appear to eat something inedible (sand, chalk, sulfur, toothpaste, raw minced meat, raw cereals, etc.), the smells of naphthalene, acetone, varnish begin to attract;
- the skin becomes dry and pale;
- some report tingling in the feet;
- spasms of the lower extremities occur;
- slight increase in body temperature.
All these symptoms may be present even with a slight decrease in hemoglobin; in cases where it has been reduced for a long period, objective symptoms include:
- tachycardia, which is accompanied by a significant increase in pulse rate;
- low blood pressure;
- heart murmurs.
If hemoglobin has decreased relatively recently, then the person primarily feels only weakness, fatigue or vitamin deficiency. In this regard, it is better to take a blood test several times a year in order to prevent subsequent painful consequences.
Low hemoglobin: what to do?
For anemia. Raises low hemoglobin: lean meat, freshly squeezed juices, dairy products, eggs, whole grains, blueberries, fish (including caviar), greens, wheat porridge, grain bread, bran, chicory, dried apricots, gooseberries, legumes, apricots, green apples , apricots, dark chocolate, plum juice, oatmeal, peas, beets, raisins, almonds, pomegranates, plums, tomato juice, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, peanut butter, pineapples (including canned ones), apricots (dried apricots) , Siberian rowan, wild strawberry, chicory, blueberry, blueberry, hazelnut, rose hip, red beet, black currant, eggplant, barley malt, etc.
How to increase hemoglobin? Video
Blood diseases. With a low level of hemoglobin, we feel weak and get tired quickly. Why does this happen and how can I fix the situation?
What is hemoglobin?
Human blood consists of plasma and cells: erythrocytes (red blood cells) and leukocytes (white blood cells). Red blood cells carry oxygen, without which cells cannot exist, and white blood cells protect the body from harmful microorganisms.
Red blood cells contain iron-containing protein - hemoglobin. Its structure contains iron ion, which, when combined with oxygen, makes our blood red in color. Moving through the circulatory system through the lungs, iron combines with oxygen and delivers it to all parts of the body. In the opposite direction, hemoglobin takes carbon dioxide from the cells and carries it through the veins to the human lungs.
Iron-deficiency anemia. What to do if your hemoglobin is low. Video
What is the normal hemoglobin level?
Hemoglobin level indications for women and men differ slightly. · Female norm: from one hundred and twenty to one hundred and fifty g/l. · Male norm: from one hundred thirty to one hundred and seventy g/l.
Low hemoglobin. Komarovsky. Video
So what can a low hemoglobin level mean?
If the level of hemoglobin in the body is low, then organs and tissues begin to suffer from lack of oxygen. This condition is called anemia or iron deficiency anemia.
SIGNS OF ANEMIA: · Pallor, · Weakness, · Dizziness, · Headache, · Shortness of breath, · Fainting, · Constantly cold hands and feet, · Drowsiness, · Heart murmur.
MAIN PRODUCTS TO INCREASE HEMOGLOBIN! Video
In addition, with anemia there may still be manifestations such as cracks on the lips, severe muscle weakness, hair loss, brittle nails and an addiction to special smells that other people find unpleasant.
Why does hemoglobin decrease?
· A decrease in hemoglobin is most often caused by dysfunctional uterine bleeding due to hormonal changes in the body, blood loss during operations and childbirth.
· Poor nutrition and stress can also cause iron deficiency anemia. The risk group, in particular, includes people who constantly resort to diets to lose weight.
Nutrition for anemia. Video
· Iron deficiency anemia can also develop when iron absorption processes in the intestine are disrupted. A similar condition occurs with chronic entritis (inflammation of the colon), as well as after an operation on the intestine, when part of the intestine is removed during which.
· Low hemoglobin levels can be a congenital condition and are often observed in older people.
Natural remedies for increasing hemoglobin. Video
LOW HEMOGLOBIN, WHAT SHOULD BE DONE?
FOLK TREATMENT. How can hemoglobin levels be restored?
To increase hemoglobin in your diet, introduce low-fat varieties of meat products. Consume freshly squeezed juices as much as possible, and especially pomegranate juice. This does not apply to the so-called. “juices - nectars”, which producers give out as juices. Increase your time outdoors.
Anemia. How to cure anemia? Video
FOLK METHODS AND RECIPES FOR TREATING LOW HEMOGLOBIN
The following will help replenish iron levels in the body: · Dairy products; · Eggs; · Whole grains; · Fish (including caviar).
How to increase hemoglobin? Hemoglobin in the blood - doctors' recommendations. Video
HOW TO INCREASE LOW HEMOGLOBIN USING FOLK REMEDIES?
In order for the body to easily accept protein, it must be combined with carbohydrates contained in vegetables and fruits. Add more dill and parsley to salads. Drink less tea and coffee. After all, they contain substances that wash iron out of the body. A diet like this replenishes iron deficiency and will help increase hemoglobin.
However, when low hemoglobin persists for a long time, this means that a disease has formed, and then diet alone is not enough. In these cases, iron deficiency is compensated with the help of medicinal preparations.
Why is iron deficiency dangerous in the body? Video
When treating, it is important to strictly observe the dosage; excessive amounts of iron in the body can cause another unpleasant disease - hemosiderosis. And that is why it is not recommended to take iron medications on your own.
Remember that it is not so difficult to develop anemia (anemia), but increasing hemoglobin is much more difficult.
How to increase hemoglobin at home. Increase in hemoglobin. Video
How can hemoglobin be raised without meat?
Hemoglobin levels can also be raised with the help of the following products: wheat porridge, grain bread, bran, dried apricots, legumes, apricots, green apples, dark chocolate, plum juice, oatmeal, tomatoes, peas, beets, raisins, almonds, pomegranates, plums, juice tomato, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, peanut butter, pineapples (including canned ones).
These products are all rich in iron and increase hemoglobin. And of the listed products, many are comparable in iron content to meat.
HOW TO INCREASE HEMOGLOBIN IN THE BLOOD? Beetroot and berry smoothie. Video
FOLK RECIPE WITH GOOSEBERRY IN PREGNANCY WITH LOW HEMOGLOBIN (FROM ANEMIA, ANALACY). Pregnant women should remember that gooseberries can fight iron deficiency anemia. Therefore, it should be included in the diet of women who are expecting a child. As a result of regular consumption of gooseberries during pregnancy, the risk of developing anemia is reduced to almost 0, and no problems will arise in the future. Pregnant women often suffer from anemia during pregnancy. Minerals and vitamins do not have time to accumulate in the body for two people at once - for the future baby and the mother. During this period, a woman needs to monitor her diet very carefully; it must contain a lot of vegetables, berries and fruits.
And if iron deficiency anemia occurs, then you should not despair; you need to include gooseberries in your daily menu.
How to really increase hemoglobin in the blood with anemia? Video
Shambhala (helba) for anemia (low hemoglobin). Tired and exhausted people will benefit from Helba to restore strength and hemoglobin levels.
TOMATOES, TREATMENT WITH TOMATOES. FOR TREATMENT OF LOW HEMOGLOBIN (ANEMIA, ANALOGY)
Anemia is a number of diseases characterized by a low content of hemoglobin in the blood. Anemia is divided into types, which differ in the deficiency of a substance in the body of one or another.
Iron deficiency in acute or chronic form, caused by blood loss, as well as breastfeeding or pregnancy, leads to rapid fatigue, dizziness, “spots” appearing before the eyes, brittle nails, hair loss, changes in appetite, etc.
So, there is anemia, which is associated with a deficiency of vitamin B12. It is caused by helminthic diseases, alcoholism, or dysfunction of the gastric mucosa. The main signs of such anemia are diarrhea and a burning sensation in the tongue.
Associated with deficiencies in vitamin B12, anemia can lead to damage to the nervous system. As a preventive measure, it is recommended to carry out timely treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
CARROTS - BEET JUICE. Benefits to the human body. Video
It is useful to take an infusion of blueberries for ANEMIA (LOW HEMOGLOBIN): two tablespoons of dry tea, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for a couple of hours, then strain and drink in equal portions throughout the day.
For stress and anemia: prepare juice from chicory: cut off the tops of the plant, wash and scald with boiling water and grind through a meat grinder. Squeeze the juice out of the resulting pulp, boil it for several minutes and store it in a glass (jar with a lid) in the refrigerator. Dissolve 1 teaspoon each of honey and chicory juice and in half a tbsp. warmed milk. Drink three times a day for a month. The result will definitely be excellent.
Is a decrease in hemoglobin dangerous for a pregnant woman or a nursing woman? Komarovsky. Video
Recipes special for increasing hemoglobin.
Choose from the following recipes the one that suits you best, and try to use it on a regular basis, as a “vitamin supplement” for your body. 1) Walnuts tbsp. and more raw buckwheat groats. grind, add a glass of honey, mix everything, eat a tablespoon every day. 2) Walnuts, honey, dried apricots, raisins - all in proportions: 1:1 - grind and mix thoroughly, eat 1 - 3 tablespoons per day (this is one of the best recipes not only for raising hemoglobin, but also for providing the body with vitamins necessary). 3) 1 tbsp. Grind walnuts, dried apricots, prunes and raisins, add honey, and add one or two lemons (you can add aloe juice instead of lemon), eat from 1 to 3 tablespoons tbsp. per day.
How to increase HEMOGLOBIN? Recipes. Video
4) One hundred ml. freshly squeezed beet juice, one hundred ml. carrot, mix and drink (hemoglobin literally rises in 2 days). 5) 1/2 tbsp. apple juice, 1/4 tbsp. beet juice and 1/4 cup carrot juice, mix and drink 1 to 2 times a day. 6) freshly squeezed apple juice 1/2 tbsp., 1/2 tbsp. homemade cranberry juice, 1 tbsp. freshly squeezed beet juice, mix and drink. 7) Raw buckwheat 1/2 tbsp., rinse, pour 1 tbsp. kefir and leave it overnight, the porridge is ready in the morning, you can eat it. 1/2 tbsp. good quality dry red wine, evaporated in a water bath for five to seven minutes, 1/4 tbsp. boiled nettle, 1 tablespoon tbsp. Ghee butter, drink warm.
freshly squeezed beet juice, one hundred ml. carrot, mix and drink (hemoglobin literally rises in 2 days). 5) 1/2 tbsp. apple juice, 1/4 tbsp. beet juice and 1/4 cup carrot juice, mix and drink 1 to 2 times a day. 6) freshly squeezed apple juice 1/2 tbsp., 1/2 tbsp. homemade cranberry juice, 1 tbsp. freshly squeezed beet juice, mix and drink. 7) Raw buckwheat 1/2 tbsp., rinse, pour 1 tbsp. kefir and leave it overnight, the porridge is ready in the morning, you can eat it. 1/2 tbsp. good quality dry red wine, evaporated in a water bath for five to seven minutes, 1/4 tbsp. boiled nettle, 1 tablespoon tbsp. Ghee butter, drink warm.
How to increase hemoglobin using folk remedies? Part 1. Video
FOLK RECIPE WITH APRICOT FOR LOW HEMOGLOBIN (ANEMIA). Apricot is a source of iron, a mineral that plays an important role in the formation of hemoglobin. In addition, apricot fruit contains copper, which helps in the absorption of iron. This improves blood circulation in the body, preventing anemia.
How to increase hemoglobin using folk remedies? Part 2. Video
FOLK RECIPE WITH APRICOT FOR LOW HEMOGLOBIN (ANABLOOD) AND VISION DETERIORATION. Drink ¾ tbsp of apricot juice daily.
TRADITIONAL MEDICINE FOR LOW HEMOGLOBIN (ANABLOOD) RECOMMENDS:
INTERNAL APPLICATION. SIBERIAN ROWAN FOR ANALACY (IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA). An infusion of berries is used as a multivitamin for anemia and exhaustion (pour 2 tablespoons of tea berries with a couple of glasses of boiling water, leave for an hour, add sugar to taste and drink in three or four doses during the day).
FOLK METHODS AND RECIPES FOR TREATING ANALACY
FOREST STRAWBERRY is a herbaceous, perennial plant, from five to fifty centimeters in height with a short brown rhizome, thin fibrous roots and long shoots, creeping shoots - tendrils. The leaves are trifoliate, basal. The flowers are white. The berry is red, fleshy, conical or ovoid in shape, the pulp of which contains small dry fruits - nuts. The berries ripen in June–July. For treatment purposes, berries are used, less often - rhizomes and leaves. Berries contain up to 10% sugar, pectic, organic acids, flavones, coloring, tannins, up to 12% essential oil, traces of vitamin B1, carotene, phytonicides, up to 60 mg% ascorbic acid, potassium, sodium, iron phosphate, calcium , aluminum, copper, manganese, chrome. The content of iron salts in berries is forty times richer than in grapes. The leaves contain up to 200 mg% ascorbic acid, traces of alkaloids, carotene, tannins. Roots and rhizomes contain up to 10% tannins. The berries are harvested when fully ripe in the morning, after the dew has dried, and also in the evening in dry weather. In wet weather or when there is dew, the collected fruits spoil quickly, and in hot weather they wither. Dry the strawberries in dryers or ovens at temperatures up to 65 degrees, laying out a thin layer of two to three centimeters on a wire rack. Typically, fruits are stored for no more than a day; at 0 temperatures, the shelf life is up to five to seven days. The leaves are collected during the flowering and fruiting period, they are torn off without petioles. Dry the fruits under canopies with good ventilation in a thin layer, laying them out on cloth or paper. Rhizomes are dug in the fall, clearing small roots.
Anemia, treatment of anemia.
INDICATIONS FOR USE. Strawberries for anemia (low hemoglobin). Fresh strawberries are used medicinally for anemia. Dried fruits are used as diuretic infusions for kidney stones and cholelithiasis, gout (which helps reduce uric acid in the body and their salts), for scurvy, gastritis, avitomonosis and uterine bleeding. Some may experience allergic rashes, similar to hives.
FOR ANALACY (ANEMIA) FEES ARE USED:
INTERNAL APPLICATION. COLLECTION AT LOW HEMOGLOBIN. Nettle leaves, yarrow flowers, dandelion root (equal amounts of all). Brew a tablespoon of the mixture with one and a half cups of boiling water, leave for three hours, and strain. Drink 3 to 4 times a day in twenty minutes. before meals. One course of treatment: two months.
COLLECTION OF THE MIXTURE FOR ANALACY (LOW HEMOGLOBIN). Nettle leaves, flowered tops of buckwheat, leaves of fireweed - tea (all equally). 3 tablespoons tbsp. Brew the mixture with a couple of glasses of boiling water, leave for three hours, and strain. Drink 3-4 times a day, twenty minutes before meals. One course of treatment: 6 to 8 weeks.
COLLECTION OF THE MIXTURE FOR LOW HEMOGLOBIN (ANANAMIUM). Nettle leaves, birch leaves (equal parts). Brew a couple of tablespoons of the mixture with one and a half cups of boiling water, leave for 60 minutes, strain, add 150 ml. beet juice. Drink 3-4 times a day, a third of an hour before meals. One course of treatment: eight weeks.
FOLK RECIPE WITH APRICOT FOR VESSELS AND HEART WITH LOW HEMOGLOBIN. Apricot and dried apricots are an excellent source of potassium to support heart health. Scientific studies have long shown that people consuming foods rich in vitamin C and potassium were less susceptible to heart disease. And dietary fiber removes excess cholesterol from the arteries, reducing the load directly on the heart. Apricot protects lipoproteins in the body from oxidation, prevents heart disease and stroke. And potassium in apricot regulates the balance of intracellular water levels, and thereby controlling blood pressure. Half a century Apricot juice will provide the body with ten% of the recommended amount of potassium for the body.
Be healthy!
Low hemoglobin: what to do? Is it possible to increase hemoglobin with food? Video
Anemia or anemia can be cured with folk remedies. Video
Similar articles:
Anemia, treatment of anemia
Atherosclerosis, treatment of atherosclerosis
Traditional medicine recipes to boost immunity
Varicose veins, treatment of varicose veins
Mongolian miracle to boost immunity
The danger of anemia and consequences
According to statistics, a third of the world's population suffers from iron deficiency anemia. This disease is especially common among women and children. There are several forms of anemia:
- Mild, in which iron-containing protein in the blood is 90-120 g/l.
- Average – up to 60 g/l.
- Severe - in this case the level drops below 60 g/l.
When hemoglobin decreases to 50 g/l, there may be a threat of acidosis - this is a shift in the acid-base balance in the body towards an increase in acidity. This condition is extremely dangerous, since over time it will lead to depression of both cardiac activity and respiratory centers.
If low hemoglobin is present for a long time in a severe form, problems with the human immune system are possible. The most common cold in this case will be difficult, with the possibility of complications. Gradually, the body loses its defense function against harmful microbes and organisms, which undoubtedly poses a great threat to health and sometimes life.
Consequences of low hemoglobin
When hemoglobin drops, the oxygen supply to cells is disrupted. As a result, such changes entail a number of negative consequences from the organs and systems of the body. First of all, hypoxia affects:
- central nervous system – depression, sleep disturbance, asthenic syndrome, hallucinations;
- immune system – the frequency of viral and infectious diseases increases;
- gastrointestinal tract – digestive disorders;
- respiratory-pulmonary system – bronchitis, asthma;
- cardiovascular system – angina pectoris, ischemic disease.
In addition, male infertility develops against the background of decreased sperm activity. The functioning of the liver and kidneys is impaired. If hemoglobin is reduced for a long period, then complications can be more severe - heart attack, stroke, encephalopathy, coma, death.
Features of the disease in men and women
In adults of different sexes, anemia manifests itself with similar symptoms, but it also has its own characteristics. With hemoglobin 50, a man experiences a decrease in virility and sometimes temporary impotence. In the fair half of humanity, the menstrual cycle is generally always disrupted, sometimes menstruation stops altogether.
One of the reasons for hemoglobin 50 in a woman may be pseudo-loss of blood, which occurs with diseases of the female organs such as uterine fibroids and the presence of cysts on the ovaries. All neoplasms have the specificity of being filled with blood, the resorption of which occurs slowly. But the function of hemoglobin cannot be fulfilled, since it is converted into another compound.
Pregnancy and anemia
The most common reason for a decrease in hemoglobin to 50 in women is pregnancy. This condition raises concerns for the health of both the mother and the unborn child.
The danger of such a disease is as follows:
- development of uterine hypotension (decreased tone and ability to contract);
- hypoxia (lack of oxygen for the child);
- the placenta is not positioned correctly;
- intrauterine growth retardation or cessation of development.
A child may be born with pathologies:
- low weight;
- underdevelopment;
- disorders of the nervous and respiratory systems;
- atrophy of individual organs and muscles;
- deviation in physical and mental development, the manifestation of which is possible after several months or even years.
Considering the seriousness of this condition, pregnant women are required to carefully monitor their health by visiting doctors. If possible, even when planning a pregnancy, you should improve your health in order to prevent negative consequences.
If left untreated
What is the risk of low hemoglobin for a woman?
The condition is considered pathological and puts a lot of stress on the body. Internal organs and all tissues suffer. The main danger is a decrease in immune defense. A woman becomes unprotected from infections and often suffers from colds. Consequences:
- In adolescence, it is important for a girl to receive iron and other elements. A lack of any substance can lead to developmental delays.
- At any age, pain appears when swallowing and in the stomach. It happens that ulcers of the intestines and stomach occur.
- Constant fatigue, low performance, lethargy.
- During pregnancy there is a risk of losing the baby. If you do not increase the indicators to normal, then a developmental disorder in the child is possible.
- Problems with skin, hair, nails.
- Decreased sex drive, irritability.
- For older people, low hemoglobin is dangerous due to loss of strength, regular dizziness, and fainting.
Advanced and severe cases can be fatal, especially in cases of heart failure and chronic health problems.
Anemia in children
In children, this disease is associated with various pathologies or a lack of vitamins and minerals in the body. Anemia is dangerous for a child due to weakened immunity: the body is vulnerable to various types of infections. Also, this disease can have an impact on the deterioration of physical and mental health. It is important to monitor your blood composition from birth and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
For a child's body under 18 years of age, the norms for iron-containing protein differ only by age; gender characteristics do not play a role, unlike in adults. The norm for a baby at 1-2 weeks is considered to be 125-206 g/l, at 1 year – 105-146 g/l. Further, the hemoglobin level increases by 1-3 g/l and by 6-8 years it reaches 110-150 g/l, and from 14 to 18 years – 115-160 g/l.
Signs of anemia in children
It is not easy for parents to identify this disease on their own. Poor appetite, fatigue, drowsiness, and absent-mindedness are perceived by them as a temporary feature and do not attract close attention. But at this time there is a possibility of metabolic disorders occurring.
Signs of anemia include:
- pallor, weakness;
- poor weight gain or no weight gain at all;
- dizziness;
- slow growth;
- frequent ARVI;
- changeability of behavior.
Such symptoms do not always indicate this disease, but it would still be useful to donate blood for a test. If an adult’s hemoglobin level decreases to 50 g/l, then a blood transfusion cannot be avoided. For children under one year old, the critical level is 85 g/l, after one year it is 70 g/l. Reduced hemoglobin is often recorded in overly active children.
Treatment methods
In order to begin treatment, it is important to try to identify the exact cause of the pathology and try to exclude it. Therapeutic measures should be aimed at both normalizing the color index, the level of iron-containing protein, and restoring the concentration of iron in the blood depot and serum.
In the presence of micro- or macrobleeding, the following are often indicated:
- correction of uterine bleeding;
- removal of hemorrhoids;
- surgical removal of fibroids;
- therapy of gastritis, enteritis, ulcers and other housing and communal services diseases.
Pathogenetic methods of treating low hemoglobin up to 50 g/l include the doctor’s prescription of drugs with B vitamins (“Neurobeks”, “Neurobion”, “Kombilipen”) and iron (“Aktiferrin”, “Maltofer”, “Ferkail”). They can be taken as tablets or syrup, but injections are more effective. The dose of medication is strictly prescribed by the doctor. It should be sufficient, but in no case excessive, so as not to cause intolerance to the drug.
In order to increase a woman’s hemoglobin from 50 g/l to normal, if the decrease has unknown etiological factors (heavy menstruation, uterine bleeding, etc.), the doctor develops anti-relapse therapy for chronic anemia. Often, with such a low value, a blood transfusion is necessary, but sometimes doctors manage to select effective drugs (“Ferrumlek”, “Sorbifer Durules”, “Totema”), which must be taken as regularly as he prescribes.
Low hemoglobin – causes and consequences in women
There are 2 main reasons for low hemoglobin in women:
- direct reduction of iron-containing protein in the blood;
- decreased ability of Hb to form a complex with molecular oxygen.
Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Blood anemia
Blood anemia is the reason why hemoglobin concentration decreases. As a rule, it is accompanied by a combined decrease in the number of red blood cells and a violation of their chemical structure.
It should be emphasized that anemia is not an independent pathology, but a symptom or consequence of a disease. There is a decrease in the woman’s respiratory activity, and in the extreme form, oxygen starvation develops.
Anemia develops as a result of:
- failure in the process of formation and differentiation of blood cells, in particular red blood cells. As a rule, this occurs with a deficiency of iron, folic acid or B vitamins, as well as with bone marrow cancer;
- excessive loss of blood, and with it red blood cells. The condition is typical for chronic bleeding, heavy menstruation, injury, fractures or surgery;
- disturbances in the absorption of nutrients in the intestines;
- gastric resection;
- chronic gastrointestinal pathologies; infectious pathologies;
- helminthic and parasitic infestations;
- abnormal increase in the process of destruction of red blood cells. In the blood of a healthy woman, red blood cells live and function for up to 4 months. For genetic abnormalities, infectious pathologies, intoxications, etc. the lifespan of blood cells decreases.
Adjustment with food
Sometimes the cause of the disease is an unbalanced diet. In this case, the following products will help cope with it:
- red meat;
- liver;
- buckwheat;
- beet;
- black currant;
- plums, apples, peaches;
- pomegranates and prunes;
- dried apricots and rose hips;
- nuts, beans;
- tomatoes;
- baked potatoes with skin.
If the cause of low hemoglobin is only a lack of iron, then with such a diet it will return to normal in 3-4 weeks.