What it is
A smear for the degree of purity is the fastest and easiest way to determine inflammatory processes and STIs - sexually transmitted infections. An accurate result can be obtained regardless of whether there are any manifestations and complaints, or whether the disease occurs in a latent form.
The procedure is absolutely painless and takes only a few minutes. The doctor makes a scraping with a disposable instrument, collecting discharge from the walls of the vagina and cervix. The sample is applied to a glass slide and sent to the laboratory. Next, it is stained using a special technique so that bacteria can be differentiated from each other.
The result of studying a gynecological smear shows the condition of epithelial cells and the presence of diseases such as vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis, cervicitis, etc. It also helps to recognize sexually transmitted pathologies, or STIs, in particular, gonorrhea and trichomoniasis.
Help: Assessment of the degree of cleanliness is necessary before further diagnostic and surgical procedures - cauterization of cervical erosion, removal of polyps, cleaning.
Cytological smear
A cytological examination is carried out to evaluate the morphological structure of cells in a gynecological smear in order to detect malignant or benign neoplasms. This is part of the medical examination in some countries around the world. The analysis does not last long, is not very expensive, and, nevertheless, helps prevent women from going to the doctor if the symptoms of the oncological process are already pronounced. After all, its peculiarity is a hidden current. Cervical cancer disguises itself as a less dangerous gynecological pathology.
When deciphering the results, it is possible to assess the level of danger facing the woman. Why do they take a smear, to detect what pathologies:
- leukoplakia - severe damage to the mucous membranes, which are lined with stratified squamous or transitional epithelium;
- erythroplakia is a precancerous condition with a high probability of mutations of ordinary cells into cancerous ones;
- the formation of polyps, which are benign neoplasms.
With the help of a cytological examination of a smear, it is possible to determine other changes. They may be normal or pathological. In the latter case, the patient is prescribed a number of additional tests. A cytogram of inflammation is compiled - the result of microscopy of epithelial cells of the vagina and cervix, indicating the presence of an inflammatory process. Its main indicator is a large number of leukocytes found in a cytological smear.
When to get examined
There are a number of indications for performing oncocytological studies. It is its results that make it possible to confirm or refute the presence of oncology. Taking biomaterial is indicated when the following pathologies are detected:
- cervical erosion - damage to the squamous epithelium;
- the inflammatory process occurring in the organs of the genitourinary system, provoked by papillomavirus infection;
- genetic predisposition to cervical cancer.
Examination for oncocytology of the cervix is indicated for women who are sexually active. A smear is taken when applying for pregnancy registration. But only if there are no oncocytology results over the last six months. If a smear analysis shows the presence of modified cells, but they are not yet malignant, the study should be repeated at least 2 times a year and even more often. Biomaterial is taken for symptoms characteristic of cervical cancer. For example, if a woman complains of bloody vaginal discharge or weakness.
Important: Routine oncocytological examination is not carried out for any indication. Its goal is to identify the oncological process at the earliest stages of its development.
Analysis methods
A gynecological smear can be tested in several ways, and testing in the laboratory uses various tumor markers. If the patient shows clear signs of a precancerous condition or already has oncology, a study using 2-3 methods is prescribed. The most highly sensitive and informative are the following:
- Leishman's method. The objects of analysis are scrapings from the cervix or cervical canal. They are cleared of mucus, stained, and then fluorescent microscopy is performed. Morphological changes in cells are indicated by a characteristic glow;
- PAP test. After taking a smear, it is fixed on a glass slide, dried and only then stained with special reagents.
Modern laboratories use liquid-based cytology, the most informative screening test. There is no need to apply the biomaterial to the glass - it is immersed in the solution, which significantly extends the shelf life and reduces the likelihood of obtaining false results. How long does it take to test for oncology? If you need results urgently, a few hours are enough. If the laboratory is very busy, you have to wait 2-5 days.
Decoding
Most often, the analysis reveals dysplastic changes, which do not yet indicate cancer. Identifying dysplasia at an early stage allows you to start treatment in a timely manner and avoid the development of complications. Thanks to a course of medications, physical therapy or surgery, all painful symptoms disappear. The doctor decides how to treat dysplasia, focusing specifically on cytology data.
Cytology smear examination is the most informative diagnostic criterion for cervical cancer
The essence of the study: how they do it
The essence of the study itself is to use the ability of bacteria to stain due to the special structure of the cell wall. This technique was first proposed by the Danish scientist Gram, who used aniline dyes followed by fixation with iodine.
Next, the sample is washed in an alcohol solution, after which some bacilli turn blue, while others become colorless. The first ones, which turn blue, have a thick cell wall and are gram-positive. The second ones are thin-walled and, accordingly, gram-negative.
After washing, a red dye is added to the sample, which gives the gram-negative bacilli a red or pink hue. Staining is provided by external membranes that create an obstacle for the dye to enter the cells. Thus, the analysis classifies microorganisms and divides them into 2 categories according to the characteristics of their cellular structure.
The laboratory assistant examines the composition of the sample under a microscope and counts the number of colored microbes, assessing their shape and size. In addition, the number of leukocytes in the field of view, epithelial cells, and mucus is taken into account. If there are key cells, then their level is determined.
If it is necessary to obtain more accurate results using the sample taken, microflora culture can be performed. In gynecology, it is required in cases where the infectious agent is present in too low a concentration, or a specific type of bacteria needs to be identified.
Comma Variabile is an opportunistic microorganism that should not be present in the smear at the first two degrees
The duration of crop cultivation depends on the type of pathogen of interest. The longest time – 15 days – for the crop to mature is for chlamydia. During the period of colony maturation, you can also find out which antibiotics it is especially susceptible to. You need to know the latter to select the optimal drug to cure the disease.
Elevated leukocytes in a smear, causes, treatment
At every consultation with a gynecologist, you need to take a smear for flora; it is always taken if the patient complains of feeling unwell; with the help of a smear you can learn a lot and then prescribe effective treatment. The analysis is carried out only before examinations, colposcopy and other procedures. Remember that the result will depend on how the analysis was taken. Using a spatula, take the secretions and spread them on the glass. Then the analysis is sent to the laboratory for examination.
A very important indicator for this analysis is the number of leukocytes in the smear; they indicate an inflammatory process. The norm is when the indicator is no higher than 15.
When a woman receives a test with elevated leukocytes, she should definitely consult a doctor; it is best to do a repeat test. In cases of inflammation, there are not many rods, but there are many cocci. If there is an increase in leukocytes in the smear, it is very important that the doctor examines you to see what the vulva, cervix, and vagina look like and what discharge is observed from the genital tract. An experienced doctor can identify inflammation by sight and smell.
When do leukocytes appear in a woman’s smear?
Along with a smear on the flora, a cytology test is taken, with the help of which you can find out whether the cervix is inflamed. Using a flora analysis, you can identify the following pathogens: fungi, gonococci, trichomanas. White blood cells in a smear can indicate the following diseases:
1. Colpitis.
2. Urethritis.
3. Adnexite.
4. Cervicitis.
5. Oncology in the genital organs.
6. Dysbacteriosis of the intestines and vagina.
If the increase in leukocytes is persistent, further investigation is necessary. It is imperative to carry out a culture for microflora, an antibiogram. Using it, you can find out about the causative agents of infection - Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus, you must determine what quantity they have, then select a drug to which these pathogens are sensitive.
Pathogenic microorganisms - chlamydia, gonococci and trichomanas can be identified using DNA diagnostics. It is used to detect herpes, HPV, cytomegalovirus. Mycoplasma and ureaplasma can be detected using culture with an antibiogram. Because they live in a woman’s body and may not cause inflammation. It is very difficult to prescribe treatment after leukocytes are detected in the blood. First you need to find out the main reason for the inflammation.
Leukocytes in a smear can show how the process is proceeding; the more leukocytes, the more dangerous the inflammation.
Rarely does the number of leukocytes reach 100. It happens that the tests show nothing, the tests are normal, but the leukocytes are still high, this indicates dysbiosis in the vagina, when the ratio of microorganisms is disturbed. In this case, you cannot use antibiotics; this can only cause harm, because this is what leads to this disease. For this disease, suppositories are used that help restore the microflora of the vagina and intestines.
Leukocytes in a smear of a pregnant woman
A pregnant woman takes her first smear when she registers. The norm is a slight increase in leukocytes, the indicator ranges from 15 to 20. If leukocytes increase, this indicates inflammation and an infectious disease.
To determine the cause, it is necessary to undergo additional examination, take a culture test for bacteria, examine the immune system and PCR.
It is not necessary that the woman contracted the infection; it could have been living in her body recently, and due to hormonal changes, the immune system began to manifest itself. That’s why it’s so important to monitor a woman’s health during pregnancy, because they can manifest themselves due to decreased immunity. Some diseases are sexually transmitted - gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, syphilis, genital herpes.
White blood cells often increase due to thrush; pregnant women are more often affected by the disease; this disease manifests itself in late pregnancy.
It is difficult to treat this disease in pregnant women, because many antibiotics are contraindicated for them; remember that inflammation can infect the uterine cavity and become a threat to pregnancy.
That is why it is so important to carefully and closely monitor your health and the condition of your baby. Any disease affects the child.
How to reduce the level of leukocytes in a smear?
To do this, you need to restore the microflora in the vagina. You can use the following medicinal herbs - aloe leaves, St. John's wort, chamomile, oak bark and red root. Douching with chlorophyllipt solution helps a lot. Warm baths will help combat the inflammatory process. You may need special suppositories - pimafucin, terzhinan, polygynax, etc.
So, leukocytes increase in the smear, if there is inflammation in the genital organs, there are cases of medical error or laboratory tests; in order to prescribe effective treatment, additional research must be done. If leukocytes increase, but the pathogen is not found, this indicates that there is dysbacteriosis in the intestines and vagina. In this case, it is imperative to take care of the microflora. Taking a gynecological smear for flora is a very important and effective research method in order to timely diagnose the condition of the female reproductive system. It is recommended that all women undergo such an analysis regularly, regardless of whether they have no or no complaints about the reproductive system. One of the important factors that helps to learn about gynecological pathology in time is leukocytes. These blood cells are of no small importance because they perform a protective function, rid the woman’s body of pathogenic microorganisms and thereby prevent the pathological process from developing. When the pathogen is identified, a special course of drug treatment will be prescribed, which should take into account the pathogenic flora, sensitivity to the drug and whether the woman is pregnant. It is necessary to carry out antibiotic therapy, but it is very important to control the entire process; this should be done by a doctor.
Interesting articles:
medportal.su
How to take a smear
A microflora test is taken by a gynecologist who conducts an examination. It can also be taken in a private laboratory, where samples are taken by junior medical staff.
A clean smear is a very simple but informative method that allows you to prevent the development of most gynecological diseases
The procedure is carried out according to a specific algorithm and consists of several stages:
- The woman sits on a gynecological chair.
- Speculums are inserted into the vagina to provide access to the walls and cervix.
- Biomaterial is collected from the back wall of the vagina.
- The sample is applied to the glass slide using streaking movements as thin as possible. This is necessary for the longitudinal arrangement of cells, in order to avoid their layering on each other.
- If the sample is planned to be sent to the laboratory later than 3 hours later, it is fixed with a special compound. Thanks to this manipulation, the cells do not deform when drying and are better preserved.
- In the laboratory, the sample is Gram stained. The most commonly used dye is methylene blue.
- The result is assessed from three points of view: leukocytes are counted, the species composition of the flora and the degree of purity are determined.
Taking a smear to determine the degree of purity is possible from one or three areas at once: the vaginal walls, urethra and cervical canal. These areas are located in close proximity, so the pathological processes in them are interconnected.
Separate tools are used for each area. The taken biomaterial is applied to 3 different glass slides.
Questions
A poor vaginal smear result is not a cause for panic or extreme concern. After all, any infectious disease that can cause a poor smear result is now completely curable. Therefore, a poor smear result is a reason for further and in-depth examination, which will reveal a hitherto hidden infection, and then undergo a course of effective treatment. That is, a poor smear result against the background of good health and the absence of clinical symptoms is a positive phenomenon, since it allows one to identify hidden and potentially dangerous infections that could hypothetically cause infertility or malignant neoplasms in the future. That is why a poor smear result should be considered as a guide to further action, and not as terrible news that literally broke out of the blue. Thus, if a woman gets a bad smear result, she needs to do the following:
- Contact a gynecologist for a detailed examination. To do this, the doctor can prescribe tests for various infections using PCR, bacteriological culture with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics, ultrasound, etc.;
- After receiving the results of all tests and examinations, you must again contact the gynecologist, who will prescribe the necessary treatment;
- After completing the course of treatment, you must contact your doctor again, who will prescribe the necessary control tests. If the results of these control tests are good, then the treatment was effective. If the results of control tests turn out to be poor, you will have to undergo an additional course of treatment.
If the result of a vaginal smear is poor, you cannot treat yourself or douche. Many women believe that a poor smear result is a consequence of poor personal hygiene and try to correct this by douching. However, douching will not help restore “purity” in the vagina, but can significantly aggravate microflora disturbances and, thus, further worsen the result of the subsequent smear.
Norms
Normally, a smear for the degree of purity shows:
- flat epithelial surface cells – up to 10;
- leukocytes – up to 10;
- intermediate epithelial cells – single;
- pseudokey cells – rare;
- the total number of bacteria is moderate or large (less often);
- mucus – in small quantities;
- lactobacilli – the majority;
- microorganisms other than lactobacilli are rare.
Deviations from the norm are considered to be the presence of:
- key and parabasal cells;
- dead epithelial cells in significant quantities;
- a large number of bacteria other than lactobacilli;
- Candida mushrooms with pseudomycelium and blastospores;
- gonococci and trichomonas;
- atypical cells that can degenerate into malignant ones. The presence of this indicator indicates the development of a precancerous condition or oncological pathology.
Purpose of a smear on the flora
If the woman is healthy, the results will indicate the presence of lactobacilli and a small number of leukocytes.
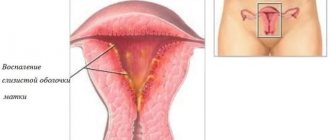
There should be no red blood cells, pathogens of trichomoniasis and gonorrhea, and Candida fungi in the tests. If they are identified, then you need to take a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test for sexually transmitted diseases. The normal number of leukocytes is up to 10 per field of view. Most often, such results indicate that you have colpitis, urethritis or endometritis. With colpitis, the vagina becomes inflamed, with urethritis, microbes cause inflammation of the urethra, and endometritis is damage to the inner layer of the uterus.
If the doctor is alarmed by something, or there is a clear deviation from the norm, he sends the patient for further examination. It is necessary to determine what pathogen caused this reaction and what antibiotic should be used to treat it.
Usually, if the smear is bad, the woman may feel discomfort, which manifests itself:
- Discharges.
- Redness of the genitals.
- Itching.
- Abdominal pain.
- Pain during sex.
But it happens when inflammation occurs hidden. It does not make itself felt in any way, but causes harm to the body. In severe cases, even infertility is possible. Some infections can increase your risk of cancer. So taking a smear test for infections on time is a necessity.
Such a simple informative analysis helps to identify many serious pathologies:
- Bacterial vaginosis.
- Vaginitis (colpitis).
- Cervicitis.
- Endometritis.
- Candidiasis.
During pregnancy, the number of lactobacilli decreases, which is due to a general decrease in immunity. To identify abnormalities in the microflora and infections in the early stages, all pregnant women are prescribed a gynecological smear. Many expectant mothers worry that a smear may harm the baby. Don’t be afraid - the doctor takes the material very carefully, without penetrating the uterus with the instrument. You will not feel any discomfort, and this examination will not affect your child in any way.
If deviations are detected, the doctor will prescribe local remedies. During pregnancy, most antibiotics are prohibited; preference is given to vaginal tablets, suppositories, creams and sitz baths. If minor deviations from the norm are detected, the gynecologist may simply leave you under observation. It is also worth considering the fact that one test taken in different laboratories may show different results. Always use the services of one trusted laboratory or clinic.
After the material for research has been obtained, it is examined under a microscope.
The size, shape, and number of cells are determined. If there are slight changes, the doctor may diagnose cervical dysplasia. Causes of this condition:
- Bad habits.
- Long-term use of contraceptives.
- Lack of vitamins.
- Onset of sexual activity before age 17.
- A large number (more than two) sexual partners.
To identify the pathology as early as possible, contact your gynecologist if you experience slight bleeding outside of menstruation and other symptoms that were not there before. With the first degree of cervical dysplasia, only its surface layer has an abnormal structure. Sometimes the doctor may decide not to treat the disease at all at this stage. A woman, especially if she has not given birth, may be left under observation. Or, if deviations in the level of sex hormones are detected, it is corrected. After this, dysplasia may disappear.
In the second degree, the abnormal cell structure also extends to the middle layer. The third degree of dysplasia is diagnosed when all layers are affected. This condition is the most dangerous and is considered precancerous. Usually in this case the patient is referred for a biopsy. If the third degree of dysplasia is detected during pregnancy, delivery is carried out by cesarean section after consultation with a gynecological oncologist.
For any degree of dysplasia, an extended colposcopy is required to clarify the diagnosis. During this procedure, the doctor examines the structure of the cervical epithelium under a microscope. The doctor gains access to it, as usual, using a gynecological speculum.
Advanced colposcopy, unlike simple colposcopy, involves the use of tests with 3% acetic acid and Lugol's solution. Such tests help identify the lesion - it is colored in a certain way. Colposcopy helps confirm the need for a biopsy or refuse it. If you have been diagnosed with cervical erosion, poor oncocytology, or genital condylomas, you will be prescribed a colposcopy. In some cases, the procedure for examining the cervix under a microscope can even be prescribed to pregnant women.
Women from this group need to be especially attentive to themselves:
- You are at risk if your mother or grandmother had CC.
- If you started having sex at age 17 or earlier.
- If you smoke.
- If you have many sexual partners.
- If you gave birth before age 17.
Based on the results of oncocytology, you may be prescribed treatment. This is not always surgery. In the early stages, cervical dysplasia is eliminated using special procedures. The radio wave method is most often used. The device removes the affected tissue without pain. The use of radio wave treatment for cervical dysplasia is possible even in young nulliparous women.
Other methods are somewhat outdated: removal with an electric knife, laser or freezing. Treatment is selected by the doctor depending on whether there was a birth, taking into account the stage of dysplasia and concomitant pathology. Most procedures today are done with the patient's comfort. These minimally invasive techniques do not damage the tissue structure, so you can carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
Why it is carried out: the study allows you to evaluate the microflora - the presence of pathogenic bacteria and their quantity.
Such an analysis, taken from a healthy woman, should show 95% of lactobacilli in the collected material. Lactobacilli produce lactic acid, thereby protecting the genitals from infections and maintaining the desired acidity. In pregnant women, the number of lactobacilli decreases, so the body’s natural defenses are weakened. In order to prevent the development of diseases that cause sexually transmitted infections, a smear during pregnancy should be taken by all expectant mothers, without exception.
To identify infections that cannot be detected by flora analysis, a smear is taken for hidden infections. One of the most common methods for detecting hidden infections is the PCR method.
Normally, the microflora of a healthy woman may contain gardnerella and candida, but their quantity should be low. Gardnerella and candida begin to actively develop when immunity decreases. The body's defenses can be weakened for various reasons:
- pregnancy;
- fatigue;
- emotional fatigue;
- the presence of a disease that the immune system is “busy” fighting.
When assessing it, four purity groups are distinguished.
- First. The reaction is acidic - pH 4.0–4.5. Most microorganisms are Doderlein bacilli (aka lactobacilli), in small quantities - leukocytes in the smear, epithelial cells. Such results indicate a healthy reproductive system.
- Second. The reaction is acidic - pH 4.5–5.0. In addition to lactobacilli, there are gram-negative bacteria - these are most often the causative agents of infections, which become discolored after laboratory staining.
- Third. The reaction is alkaline or slightly acidic - pH 5.0–7.0. Mainly bacterial microflora, epithelial cells are also in large numbers. Several lactobacilli were detected.
- Fourth. The reaction is alkaline - pH 7.0–7.5. There are no lactobacilli, the flora is represented by pathogenic organisms. There are a large number of leukocytes in the smear. This analysis indicates inflammation of the vaginal mucosa.
If the result is bad (group 3 or 4), your doctor may refer you for a repeat test or culture to confirm the results.
Decoding
Results may vary from laboratory to laboratory. Depending on which laboratory you took the smear from, the norm may vary. Since research methods may differ in each individual laboratory, the results will be different. It is advisable to take all tests in one laboratory so that you can observe changes over time and these changes are not associated with a change in the laboratory where you take tests. Decoding must be carried out by a doctor.
To indicate the number of bacteria when examining smears from the urethra, vagina, as well as when analyzing a cervical smear, CFU/ml is used. These units of measurement are read as the number of colony-forming units in one milliliter of liquid.
If there are “wrong” cells as a result of cytology analysis of a cervical smear, the doctor uses a special term: dysplasia.
Dysplasia is a condition of the cervix in which some of the cells have a damaged structure. This means that the cells can develop into cancer. Therefore, such a pathology may be a precancerous condition.
The risk of developing pathology increases with:
- smoking;
- a large number of births;
- long-term use of intrauterine and hormonal contraceptives;
- lack of vitamins;
- the presence of sexually transmitted infections (especially papillomavirus);
- early sexual activity (up to 16 years);
- childbirth (up to 16 years);
- a large number of sexual partners (three or more);
- genetic predisposition.
Cervical dysplasia is caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) types: 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33 and 35.
Signs may include:
- frequent inflammatory processes;
- spotting bloody discharge;
- bleeding after sexual intercourse or when using tampons.
Some women with dysplasia experience pain in the lower abdomen.
Regardless of age, there are factors that increase your risk of cervical cancer. Their combination and prolonged “effect” on the body reduce the body’s defenses in the fight against the disease, even in the early stages of development.
Flora smear is an effective diagnostic tool for assessing the nature of inflammation of the genitourinary canal
Decoding
Since a smear to determine the degree of vaginal cleanliness can be taken from different points, they have their own designation:
- V is for vagina;
- C – cervical canal;
- U – urethra, urethra.
For each point, its own indicators are indicated, and the standards may vary slightly.
Normally, pathogens should be absent regardless of the place where the biomaterial is collected
The microflora in most cases contains epithelial cells, leukocytes, Gram-positive Dederlein bacilli (lactobacillus) and mucus. All these components in a certain ratio indicate a norm or deviation.
Epithelium
Squamous epithelial cells line the inner surface of the vagina and cervix. Their number also depends on the time of the menstrual cycle. The detection of a large number of such cells may indicate the development of inflammation in vaginitis, urethritis, and cervicitis. In the absence of epithelial cells, we are talking about a hormonal imbalance due to a deficiency of sex hormones.
Leukocytes
These cells take an active part in the elimination of harmful microorganisms. The presence of a small number of leukocytes is allowed, but no more than 10 in the field of view, if a smear is taken from the walls of the vagina.
When analyzing a smear from the cervical canal, the maximum number of cells is 30. A higher concentration indicates the likelihood of an inflammatory process, since the “work” of leukocytes is to absorb pathogens (phagocytosis). If there are a lot of the latter, then the level of leukocytes increases accordingly.
Useful sticks
Dederlein's “vaginal bacilli” normally occupy a dominant position and far outnumber all other microorganisms. They help maintain a normal environment through the synthesis of lactic acid. In addition, lactobacilli compete with other (pathogenic and opportunistic) microbes for food and living space.
Lactobacilli produce special substances to destroy competing bacteria and hydrogen peroxide, which slows down the growth of the latter. There are about 130 species of lactobacilli that live in different environments, but all of them have the property of producing lactic acid. 20 species of them can live in the vagina, but, as a rule, women have no more than 2.
When the concentration of lactobacilli decreases, bacterial vaginosis, or dysbiosis, begins to develop.
Slime
Mucus is also an obligatory component of microflora, but in a very small volume. This specific substance is produced in the cervical canal of the cervix and is necessary, among other things, to maintain the viability of sperm that enter the female genital tract.
The properties and consistency of vaginal mucus depend on the level of sex hormones
Help: The volume of cervical mucus varies depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle: the longer the time remains before ovulation, the less it is synthesized.
If the third degree of vaginal cleanliness or the fourth is diagnosed, pathogenic organisms may be found in smears - Trichomonas, fungi, gonococci, gardnerella, etc.
Smear for latent infections and polymerase chain reaction
Why it is carried out : allows you to detect infections that cannot be detected by analyzing a smear for flora
In 1983, American biochemist Kary Mullis developed the polymerase chain reaction method, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize. Thanks to the scientist, it became possible to “recognize” bacteria and viruses by sight, even in their minimal quantities. Polymerase chain reaction is often called PCR diagnostics. PCR analysis and PCR smear are also synonymous. A smear, scraping or urine sample taken for analysis can reveal hidden diseases.
Polymerase chain reaction is a biological research method in which a section of DNA is replicated in the laboratory.
Why is PCR analysis needed? When examining smears, it is necessary to identify what type of infection causes the disease. But sometimes there are so few bacteria that it is impossible to recognize them. In such cases, PCR diagnostics of infections comes to the rescue.
For analysis, a section of bacterial DNA is taken and cloned many times. When the DNA “grows”, it is possible to determine what type of bacteria or fungi the laboratory technician is dealing with.
PCR diagnostics of infections gives an accurate result. It allows you to identify not only the genus, but also the type of bacteria: for example, not only to say that the fungus is of the genus Candida, but also to clarify that it belongs to Candida albicans. If the exact type of infection is not determined, treatment may not be effective.
PCR diagnostics are often used to test smears for sexually transmitted infections. Most sexually transmitted diseases, such as gardnerellosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis, may not show signs in the early stages of development. Symptoms appear in later stages. Thanks to PCR analysis, sexually transmitted infections can be detected at the initial stage of development and, accordingly, quickly cured.
When carrying out such an analysis, viral infections such as hepatitis or papilloma can also be detected. Other methods can detect not the virus itself, but only the presence of its metabolic products or antibodies to it.
The polymerase chain reaction method allows you to detect infections in any environment: in blood, urine, saliva, and on mucous membranes. In addition, thanks to PCR analysis, viruses are isolated in soil and water.
Advantages of polymerase chain reaction:
• accuracy of infection detection; • the ability to isolate the virus (and not decay products or antibodies to it); • a small amount of test material is sufficient (even in the presence of one pathogen cell); • the ability to detect infection in any environment (urine, blood, saliva); • speed of analysis; • the only method for isolating some infections
4. Pap test or cytological smear
Why it is performed : allows you to diagnose cervical cancer.
The Pap test has different names: a smear for cytology, as well as a test, analysis or smear according to Papanicolaou, a smear for atypical cells. The test is named after the Greek scientist who first used this method. To perform a Pap test, a swab is taken from the cervical canal (cervix) during an in-chair gynecological examination.
A cytological smear in a woman over 30 years of age is a mandatory annual test. Cervical smear results help diagnose cervical cancer, the second most common cancer among women.
How is a smear taken for cytology?
Several factors can affect the results of a smear test. To get a reliable result, refrain from going to the toilet 2-3 hours before taking a smear. Otherwise, you will wash away the epithelium and bacteria that are important for examining a vaginal smear.
To ensure accurate smear results, 48 hours before the test:
- don't have sex;
- do not douche (so as not to wash the vaginal contents);
- do not use vaginal contraceptives (spermicidal creams, ointments, foams);
- do not take baths;
- Do not use tampons or vaginal suppositories.
The interpretation of the smear and, accordingly, the success of treatment depend on whether the woman followed the requirements listed above. A Pap smear can be taken on any day of the cycle when there is no menstrual flow.A smear is taken by a gynecologist during an examination on a chair.
In this case, the doctor uses a speculum and an Eyre spatula - a special plastic stick. Taking swabs takes no more than two minutes. The procedure is painless.
Smears are collected in three places - possible foci of infection: a smear is taken from the cervical canal (cervix), from the vagina and urethral opening.
A smear examination is carried out by examining it under a microscope or bacteriological culture. In most cases, women do not experience any discomfort after a smear. Only occasionally may spotting from the vagina and painful sensations in the lower abdomen be observed. They should go away in a few hours.
There is no need to abstain from sex after a smear. Starting from the age of 18, even if a girl is not sexually active, experts recommend undergoing annual preventive examinations and taking a smear for oncocytology. And those who are sexually active, regardless of age, are advised to visit a gynecologist at the beginning of an intimate relationship. To detect cervical cancer in the early stages of development, after 30 years of age, be examined by a gynecologist at least twice a year.
Preparation Tips
Tip #1
Two days before the test, it is not recommended to use medications in the form of vaginal suppositories, tablets and other topical agents. You cannot douche for 2-3 hours.
Tip #2
You should come for analysis no earlier than 14 days after finishing treatment with antibiotics and antimycotic (antifungal) agents. For two or three days, sexual intercourse is excluded.
The best period for taking a smear to determine the degree of purity is 10-20 days of the monthly cycle. At this time the results will be most accurate.
FAQ
Where can I get a smear test and how much does it cost? Analysis for the degree of purity is done in any antenatal clinic and paid clinics. On average, the cost of the study is 300 rubles, but in commercial centers it can be higher. For example, in Invitro laboratories this test is carried out “in combination” with tests for STIs. A smear for microflora + 14 infections costs 6,240 rubles, a smear for microflora + 8 infections costs 3,920 rubles.
Do I need to take a control smear again after treatment? A repeat test is required. Until the results are received, doctors advise abstaining from intimate relationships; in some cases, the man may need to be examined and treated.
When should I take a smear, are there any special indications? Yes, a smear for cleanliness, or microflora, is taken when signs of inflammation appear - unusual discharge, itching and soreness in the vagina, during treatment with hormonal drugs and immunosuppressants. Such an analysis is also prescribed in the case of long-term antibacterial therapy and is carried out during a preventive examination. During pregnancy, it is done three times - when the woman comes for the first time and registers, then at 30 and 36 weeks.
Reminder for those planning to take a smear test
How to prepare for a smear on the flora and what you should not do before the test should be remembered right now, because compliance with the rules and hygiene standards is the key to the correct and reliable result of the study and the subsequent prescription of treatment.
- A vaginal smear for flora involves stopping taking any vaginal medications for three days and abandoning all antibacterial agents.
- A smear for microflora in women or any other type of smear is not given during menstruation or 1-2 days after its end.
- Before the analysis (the night before and in the morning), it is forbidden to wash or douche.
- It is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse.
A smear in gynecology is more than just a necessity, because such tests are vital. Timely detection of diseases is the key to fast and effective treatment. Therefore, do not neglect the rules, preventive methods and visit your gynecologist regularly.