Breast diseases are the most common pathology faced by middle-aged and older women. Almost 15% of them are cancer. This means that effective preventive screening of the population is necessary to detect the disease at an early stage of development. The main one is mammography.
Breast diseases are the most common pathology faced by middle-aged and older women.
Breast mammography is an X-ray examination method that has a high sensitivity and specificity. This examination is available to all segments of the female population, is organized en masse in medical institutions and is the “gold standard” for detecting tumors.
Indications
Mammography is performed on all older women at regular intervals.
A palpable formation in one of the glands is an indication for screening.
Also, an extraordinary study is prescribed if there are certain indications, such as:
- palpable hard or soft formation in one of the glands;
- visual deformation of the nipple or any other area;
- the appearance of blood when pressing on the nipple;
- local pain, signs of swelling, change in skin color, violation of symmetry on both sides.
Women of the young age category are referred for mammography under the following conditions:
- risk group for breast cancer (close relatives have been diagnosed with a malignant neoplasm);
- cancer of the uterus or ovaries;
- inability to get pregnant;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- surgical interventions on mammary organs in the past.
What does breast mammography show?
Mammographic imaging of the mammary glands may show cysts, mass formations (tumors), and calcifications. The general type of structure of the organ is also assessed (glandular, fibro-fatty, mixed with a predominance of one of the components). Attention is paid to the milk ducts, their structure and diameter.
Visualization of the mammary organs can show cysts, space-occupying formations (tumors), and calcifications.
Some mammographs are equipped with equipment for a needle biopsy, which is performed immediately to confirm or exclude the malignant nature of the process.
When to do a mammogram of the mammary glands?
Mammography is carried out as a preventative measure for all women over 40 years of age once every 2 years. At the discretion of local institutions for the female population over 50 years of age - once a year.
In addition, there are unscheduled indications for this type of examination.
Carrying out a mammogram while breastfeeding is completely acceptable.
During pregnancy at any stage, it is preferable to use the ultrasound method due to the absence of side effects, primarily radiation exposure to the body of the mother and fetus. Carrying out a mammogram during breastfeeding is quite acceptable, but it is not very informative for a doctor. It is recommended to use other auxiliary studies.
It is considered most correct to undergo a mammological examination on days 5-13 of the menstrual cycle, i.e. in the first phase. In the second phase, the breast tissue undergoes some hormonal changes: the ducts expand, the structure of the glandular component changes, and swelling of the soft tissues may appear. In this case, the result may be unreliable, and the examination will be endured with a feeling of discomfort and pain.
During menopause, mammary organs can be examined at any time.
Comparison of ultrasound and mammography
Thus, both methods have both positive and negative sides. To find out which is better, ultrasound or mammography, you need to compare them:
- Operating principle. Mammography is based on the use of X-rays, and ultrasound uses ultrasonic waves.
- Age of patients. Mammography is performed for women only after 40 years of age, but ultrasound can be done for everyone.
- Effect on pregnancy and infant feeding. Mammography, unlike ultrasound, cannot be performed during this period.
- Safety. During mammography, the patient receives a small dose of radiation; ultrasound examination is safe.
- Information content. It is impossible to unequivocally answer the question of what is more informative, since each of the studies can help diagnose diseases that are difficult to detect by other methods. Thus, mammography is indispensable for studying the condition of the milk ducts, and ultrasound is a means for performing a biopsy, and also allows you to assess the condition of the axillary lymph nodes.
- Soreness. When undergoing a mammogram, minor discomfort is possible, but there is none when performing an ultrasound.
- Gland size. There are difficulties in performing mammograms on women with very large or very small breasts. Unlike mammography, when performing an ultrasound, the size of the gland does not play a role.
- Accuracy of the result. With mammography, the resulting image is much clearer and the results are more accurate. Ultrasound has certain resolution limits.
- Directionality. Mammography is the main method for examining the milk ducts. Ultrasound is used to control the biopsy.
- Possibility of false result. This possibility remains when diagnosing using both methods.
To summarize the above, it can be noted that it is impossible to choose between mammography of the mammary glands or ultrasound of the mammary glands. Reviews from doctors about the diagnostic qualities of each method indicate that both of them are good in their own way. That is why these studies are complementary and, when used together, allow the doctor to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment. This is especially true for women who have reached the age of forty.
How to prepare?
No special measures are required before the manipulation. The results of mammography are not affected by food or liquid intake. The only recommendation is to avoid using cosmetics for the skin of the axillary area on the day of the study.
Before the procedure, you should remove all neck jewelry, raise your hair, and completely free your chest from clothing.
The radiologist or laboratory assistant warns the woman about all possible side effects, asks the day of the menstrual cycle, and asks about pregnancy at the time of the mammary gland examination.
To correctly interpret changes in the mammary organs, you need to have with you the protocols of previous studies (mammography, ultrasound, MRI).
The essence of ultrasound
The main essence of diagnostics is based on the ability of biological material to reflect ultrasound waves emitted by high-frequency sensors. After processing the incoming signals, an image of the structure of the mammary glands appears on the monitor screen, displaying the locations of the pathological areas.
Why is an ultrasound scan prescribed for breast pathologies? Using ultrasound monitoring, the condition of the breasts in women of any age is studied. The technique is most informative for the following types of tumors:
- Cysts.
- Lipomas.
- Fibroadenomas.
- Tumors with fluid inside.
For a certain clinical picture, another type of ultrasound monitoring can be used - the Doppler method, which has more extensive technical capabilities.
The best time to perform an ultrasound is considered to be the period from 5 to 10 days of the menstrual cycle.
Main advantages of the method
What is better to do an ultrasound or mammography of the mammary glands? In principle, the question is not which of them is more effective. It is important to consider that in some cases mammography may be contraindicated for some reason or it may be necessary to clarify the information obtained through another diagnostic procedure.
Ultrasound examination has a number of advantages:
- It is simple and accessible.
- Detects the smallest formations of anomalous origin.
- It allows not only to visualize the structural features of breast tissue and pathological areas, but also the degree of their echogenicity.
- Suitable for women of any age with different breast sizes (for mammography there are restrictions on the size of the bust due to the fact that a very large gland cannot be fully reflected in the image).
- Determines the presence of internal injuries and inflammation in the breast tissue.
- It is used during puncture to control the process being performed.
- Allows you to study in detail the condition of the lymph nodes and detect metastases in them.
- If a puncture is necessary, it is believed that ultrasound is preferable to an x-ray procedure.
- Analyzes and establishes the degree of quality of blood circulation in the tissues and vessels of the mammary gland and tumor.
- Provides the specialist with the opportunity to examine the structure of the mammary gland from different angles.
- Suitable for pregnant women as it does not have a harmful effect on the fetus.
- It has no restrictions on the frequency of its passage.
- The reliability of ultrasound examination results is 70-80%.
How is a breast mammogram done?
Mammography is carried out in the X-ray room, where the mammography machine is located. The woman is shown how to position herself next to him. The position depends on the type of equipment (standing or sitting). Next, a protective apron made of lead material is placed on the waist area, covering the lower abdomen. The mammary glands are placed on a plate intended for this purpose, and the chest is pressed on top with a similar plate. Next, the x-ray technician leaves the room and turns on the machine remotely. Exactly the same actions are repeated on the other side. The whole procedure takes no more than 5-10 minutes.
The mammary glands are placed on a plate intended for this purpose, and the chest is pressed on top with a similar plate.
If a pathology is detected, the woman may additionally undergo radiography in a different projection - lateral and/or oblique. At the discretion of the doctor, a targeted mammography is possible, when the affected area of the gland is directly imaged on an enlarged scale.
A photo with a description can be received on the same day. Some clinics are equipped with digital equipment that provides more detail in the resulting image. All information can be saved on electronic media and used at any time.
On the first day, a woman may complain that her breasts hurt after a mammogram. This is due to the mechanical pressure of the plates, does not last long and eventually goes away on its own.
Other X-ray examinations should be rescheduled on this day so as not to exceed the permissible radiation dose.
Mammography
This examination method is radiographic, that is, a special X-ray machine is required to implement it. The principle of mammography is that the tissues and organs of the body have varying degrees of transmission of X-rays. Consequently, by the intensity of the darkening and its specific density, one can assess the presence, localization, and stage of development of the process.
A special X-ray machine - mammograph is designed in such a way that the breast tissue is compacted between two plates of special material. This is done in order to compact the tissues to be examined as much as possible. X-rays passing through the changed areas of the organ are delayed. The image shows a thickening or darkening. Its intensity can tell the doctor a lot about the structure and nature of the tumor.
The presence of an image is a significant advantage of this method, since it allows the patient to deliver this data on an objective medium for consultation with specialists. Digital technologies have significantly expanded these possibilities. Survey data can be transmitted using storage media.
Mammographic examination is carried out in two planes. This is necessary for the most accurate determination of the location, size, and complexity of the tumor. An important advantage of mammography is the ability to select material for biopsy examination directly during the examination. This means that the mammograph is equipped with special equipment to take a microscopic piece of tissue from the pathological lesion for histological analysis.
It is histological analysis that reveals the nature of the cell structure. It is definitive for establishing the benignity or malignancy of a neoplasm.
The disadvantages of X-ray examination of the mammary glands include:
- the lack of equipment for this examination in many medical institutions due to its bulkiness, high cost, and the need for special re-equipment of the premises;
- presence of radiation exposure to the body;
- the impossibility of using this method to establish problems with the blood supply to the organ.
Radiation, which is inevitably present during X-ray examination, is contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women. Therefore, it cannot be assigned to this contingent.
Then it is possible to conduct clarifying examinations using ultrasound.
Mammography or ultrasound of the mammary glands - which is better?
Both methods, mammography and ultrasound, are highly accurate and specific for the presence of breast tumors. Ultrasound is preferable if visualization of areas located near the chest from different angles is necessary. These areas are difficult to reach for x-rays.
In addition, the ultrasound method more accurately differentiates the cystic and solid components of the tumor, identifies small pathology, and shows the presence of blood flow. It is also more informative in young females due to the increased density of organ tissue at this age. Ultrasound can be used at any stage of pregnancy.
Ultrasound is preferable if visualization of areas located near the chest from different angles is necessary.
Ultrasound allows you to analyze the size and shape of lymph nodes - an important marker for differential diagnosis between benign and malignant formations.
However, mammography makes it possible to detect single or multiple small calcifications, extensive tissue restructuring, and precise identification of the type of cyst, which is impossible with ultrasound.
Thus, both studies are complementary to each other. Combining them together significantly increases the accuracy of diagnosis and should be used when identifying pathology.
Mammography or ultrasound of the mammary glands?...Let's figure it out together!
Mammography or breast ultrasound? Let's figure it out together!
Breast examination is often performed in two ways: mammography or ultrasound. The methods differ markedly in several respects, which gives rise to debate as to which is better?
Modern research digital mammography is an X-ray examination that allows you to obtain images to study the mammary glands in several projections.
The advantage of the technique is the detail of the data obtained, thanks to which it is possible to identify the slightest changes in tissues. Mammography is a screening method, the procedure does not take more than 20 minutes, and the results are provided immediately.
In the clinical diagnostic center Medpomosch 24, in the radiation diagnostics department, digital mammography is represented by the latest generation digital X-ray full-format mammograph Brestige, which is characterized by low radiation exposure and provides excellent visualization. The results can be saved on electronic media, this is very convenient for further examination of the patient.
Image quality is the absolute criterion for success in the early detection of breast cancer.
Ultrasound examination of the mammary glands
Ultrasound is the study of organs and tissues using ultrasound “waves”. Passing through tissues of different densities, or rather through the boundaries between different tissues, ultrasound is reflected from them differently. A special receiving sensor records these changes, translating them into a graphic image that can be recorded on a monitor or special photographic paper.
The ultrasound method is simple and accessible and has no contraindications. Ultrasound can be used repeatedly throughout the entire period of observation of the patient for several months or years. Moreover, the study can be repeated several times within one day if the clinical situation requires it.
The ultrasound examination method makes it possible to detect space-occupying formations measuring 0.1 cm in diameter (cyst, fibroma or suspected fibroadenoma), with their clear localization and the possibility of puncture biopsy.
This method is most effective for detecting tumors in the early stages of their verification and the possibility of selecting the optimal treatment, either conservative or surgical.
Ultrasound, due to its high information content, non-invasiveness, speed of execution, and the possibility of repeated repetition without harm to health, occupies one of the main places among other research methods.
Advantages of ultrasound:
- High throughput
- Radiation safety
- Can be used when examining pregnant and lactating women
Ultrasound examination of the mammary glands, like other ultrasound techniques, is so safe that the procedure can be performed an unlimited number of times.
However, unfortunately, ultrasound examination is inferior to mammography in accuracy, especially in identifying small “formations”.
Naturally, in the vast majority of cases, patients are referred for ultrasound examination. Those women who have “problems” identified by ultrasound are required to undergo clarifying studies, primarily mammography. In addition, all patients over the age of 40 are sent for mammography.
In general, in modern medicine it is impossible to imagine diagnosing tumors, inflammations, or damage with only one method. Medpomosch 24 clinical diagnostic centers have everything you need to conduct any of the above examination methods.
Decoding the results
The results of mammography are assessed by a radiologist. The conclusion is issued on the same day. The research protocol describes the types of tissues that make up the mammary gland (fibrous, glandular, fatty), their relationship with each other, homogeneity or heterogeneity of the structure.
The shape of the organ is analyzed: round, oval, lobed or irregular. The size of the ducts is indicated (normally up to 0.4 cm in women of childbearing age, up to 0.2 in menopause), whether they are straight or convoluted, contain homogeneous or inhomogeneous contents, in which area they are better developed.
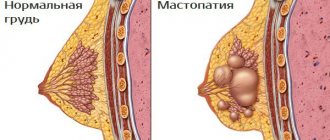
The age of the patient must be taken into account. In women over 40 years of age, involution processes begin (the glandular component is gradually replaced by fibro-fatty component). Mammography for fibrocystic mastopathy shows that during this period the glandular component predominates.
If during this period the glandular component predominates according to mammography, then fibrocystic mastopathy is diagnosed.
Dilated ducts and cysts are also clearly visible on x-rays. The doctor describes in detail their location (using a watch dial for convenience), diameter, contours, and internal contents. Types of cysts are presented as simple and complicated (festering).
The space-occupying lesion stands out quite well on the mammogram, as it is accompanied by a darkening symptom on the X-ray film. Its presence is confirmed in two projections. If visualization occurs in only one projection, then they speak of a focus of compaction in the mammary gland.
Tumors are described qualitatively by analogy with cysts, only the contours (even, uneven, presence of a capsule), density (low, mixed, high, asymmetrical), the presence and main characteristics of calcifications are analyzed in more detail.
Dilated ducts and cysts are also clearly visible on x-rays.
It is now customary to assess the condition of the mammary organs according to the international system for describing and processing data BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System), which is used in most countries.
The resulting changes are expressed as points. This algorithm accurately indicates to the attending physician further tactics for managing the patient and the necessary therapeutic measures. BI-RADS creates continuity between all treatment and diagnostic links that a woman goes through.
The scale includes 7 categories: 0 and 3 – cases subject to auxiliary research, re-monitoring after six months, 1 and 2 – sent to the treating gynecologist, 4 and higher – consultation with an oncologist, fine-needle biopsy is recommended.
The quality of the examination also depends on the experience and training of the specialist. In addition, there is a small percentage of false-positive diagnoses, which once again confirms the need for an integrated approach to the examination.
Signs of a benign tumor on a mammogram
Mammography can differentiate or suspect the nature of the formation. The main disadvantage is the difficulties encountered in women under 35 years of age due to the increased density of the organ parenchyma.
Among benign focal changes in the mammary gland there are lipoma, fibrolipoma, and leaf-shaped fibroadenoma.
Among benign focal changes in the mammary gland there are lipoma, fibrolipoma, leaf-shaped fibroadenoma, fibroadenolipoma, etc. They are characterized by the following signs:
- clearly defined, smooth boundaries;
- shape in the form of a circle, oval or lobes;
- homogeneous structure;
- absence of small calcifications;
- low density.
Signs of a malignant tumor on a mammogram
Breast cancer appears on mammography with certain properties:
- irregular or lobed shape;
- fuzzy (blurry), uneven contours;
- asymmetrical density;
- germination into healthy tissues;
- violation of architectonics;
- the presence of a local accumulation of small (up to 1-2 mm) calcifications in the structure or duct;
- enlargement and pathological changes in lymph nodes;
- thickening, swelling of the skin and subcutaneous fat layer above the tumor.
Other distinctive signs of malignant pathology in the mammary glands are the lack of compressibility and mobility of the formation, the vertical orientation of germination into the organ.
Thus, mammography of the mammary glands is a diagnostic technique that can establish the correct diagnosis as early, effectively, non-invasively, accurately, and easily as possible. In complex or doubtful cases, examination of the mammary organs should be carried out in combination with other methods.
Ultrasonography
The ability of ultrasonic waves to be reflected with varying degrees of intensity from structures of the body that differ in their structure formed the basis of this method of medical diagnostics. Examination of the mammary glands using ultrasound is widespread and helps establish a diagnosis in cases where it is contraindicated or impossible to examine the patient using mammography.
To carry out this method, it is enough to have an ultrasound diagnostic device, which is available in almost every clinic today. No preparation is required for the examination; patients must be in a supine position, which is much more comfortable than a mammographic examination, which is performed while standing.
A special gel is applied to the skin of the mammary gland, enhancing the adhesion and conductivity of tissues for ultrasonic vibrations. The mobility of the sensor allows you to examine the organ from all sides, in several planes. Ultrasound makes it possible to determine the intensity of blood flow in a particular area of the mammary gland, which is important for some diseases. In addition, ultrasound has no contraindications, such as pregnancy or breastfeeding, since there is no radiation, similar to an X-ray machine.
A significant drawback of examination using ultrasound not only of the mammary glands, but of any other organ, is the direct dependence of the information content of the result on the qualifications of the specialist conducting the diagnosis itself. Lack of experience and inattention to any detail can lead to an incorrect diagnosis and missing an important point. As for the examination of the mammary glands, it is possible to miss an area or overlook any piece of tissue.